使用 PyTorch Fully Sharded Data Parallel (FSDP2) 和 Ray Train 入门#
完成时间: 30 分钟
本模板展示了如何通过集成 PyTorch 的 Fully Sharded Data Parallel 来实现内存和性能的提升。
PyTorch 的 FSDP2 实现了模型在节点间的切分,允许在内存占用远小于标准 Distributed Data Parallel (DDP) 的情况下分布式训练大型模型。有关 FSDP2 的更详细概述,请参阅 PyTorch 官方文档。
本教程提供了一个全面的分步指南,介绍如何将 PyTorch FSDP2 与 Ray Train 集成。具体而言,本指南涵盖了以下内容:
一个图像分类模型的实际训练示例
配置 FSDP2 以通过混合精度、CPU 卸载、切分粒度等来缓解内存不足 (OOM) 错误
使用 PyTorch Distributed Checkpoint (DCP) 保存和加载模型检查点
使用 PyTorch Profiler 进行 GPU 内存分析
加载分布式模型以进行推理
注意: 此笔记本使用 FSDP2 的 fully_sharded API。如果您使用的是 FSDP1 的 FullyShardedDataParallel,请考虑迁移到 FSDP2 以获得更好的性能和功能,例如更低的内存使用率和 DTensor 集成。
Anyscale 特定配置
注意: 本教程针对 Anyscale 平台进行了优化。在开源 Ray 上运行时,需要额外的配置。例如,您需要手动
- 配置 Ray 集群:设置多节点环境并管理资源分配,而无需 Anyscale 的自动化。
- 管理依赖项:在每个节点上手动安装和管理依赖项。
- 设置存储:配置自己的分布式或共享存储系统以进行模型检查点保存。
示例概述#
为了演示,本教程将 Ray Train 与 FSDP2 集成,并使用一个在 FashionMNIST 数据集上训练的 Vision Transformer (ViT)。选择 ViT 是因为它具有清晰、可重复的块结构(Transformer 块),非常适合演示 FSDP2 的切分能力。
尽管此示例相对简单,但 FSDP 的复杂性可能导致训练过程中出现常见挑战,例如内存不足 (OOM) 错误。本指南通过提供实用的技巧,根据您的具体用例来提高性能和降低内存利用率,从而解决常见问题。
1. 软件包和模型设置#
安装本教程所需的依赖项
%%bash
pip install torch
pip install torchvision
pip install matplotlib
# Enable Ray Train V2 for the latest train APIs
import os
os.environ["RAY_TRAIN_V2_ENABLED"] = "1"
# Profiling and utilities
import torch.profiler
import tempfile
import uuid
import logging
# Set up logging
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
模型定义#
以下函数初始化一个为 FashionMNIST 数据集配置的 Vision Transformer (ViT) 模型
# Computer vision components
from torchvision.models import VisionTransformer
from torchvision.datasets import FashionMNIST
from torchvision.transforms import ToTensor, Normalize, Compose
def init_model() -> torch.nn.Module:
"""Initialize a Vision Transformer model for FashionMNIST classification.
Returns:
torch.nn.Module: Configured ViT model
"""
logger.info("Initializing Vision Transformer model...")
# Create a ViT model with architecture suitable for 28x28 images
model = VisionTransformer(
image_size=28, # FashionMNIST image size
patch_size=7, # Divide 28x28 into 4x4 patches of 7x7 pixels each
num_layers=10, # Number of transformer encoder layers
num_heads=2, # Number of attention heads per layer
hidden_dim=128, # Hidden dimension size
mlp_dim=128, # MLP dimension in transformer blocks
num_classes=10, # FashionMNIST has 10 classes
)
# Modify the patch embedding layer for grayscale images (1 channel instead of 3)
model.conv_proj = torch.nn.Conv2d(
in_channels=1, # FashionMNIST is grayscale (1 channel)
out_channels=128, # Match the hidden_dim
kernel_size=7, # Match patch_size
stride=7, # Non-overlapping patches
)
return model
2. 定义训练函数#
以下是协调 FSDP2 训练过程的主训练函数。后续部分将实现此训练循环中使用的每个辅助函数。首先,进行训练函数所需的导入
# Ray Train imports
import ray
import ray.train
import ray.train.torch
# PyTorch Core import
import torch
# PyTorch training components
from torch.nn import CrossEntropyLoss
from torch.optim import Adam
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
def train_func(config):
"""Main training function that integrates FSDP2 with Ray Train.
Args:
config: Training configuration dictionary containing hyperparameters
"""
# Initialize the model
model = init_model()
# Configure device and move model to GPU
device = ray.train.torch.get_device()
torch.cuda.set_device(device)
model.to(device)
# Apply FSDP2 sharding to the model
shard_model(model)
# Initialize loss function and optimizer
criterion = CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = Adam(model.parameters(), lr=config.get('learning_rate', 0.001))
# Load from checkpoint if available (for resuming training)
start_epoch = 0
loaded_checkpoint = ray.train.get_checkpoint()
if loaded_checkpoint:
latest_epoch = load_fsdp_checkpoint(model, optimizer, loaded_checkpoint)
start_epoch = latest_epoch + 1 if latest_epoch != None else 0
logger.info(f"Resuming training from epoch {start_epoch}")
# Prepare training data
transform = Compose([
ToTensor(),
Normalize((0.5,), (0.5,))
])
data_dir = os.path.join(tempfile.gettempdir(), "data")
train_data = FashionMNIST(
root=data_dir, train=True, download=True, transform=transform
)
train_loader = DataLoader(
train_data,
batch_size=config.get('batch_size', 64),
shuffle=True
)
# Prepare data loader for distributed training
train_loader = ray.train.torch.prepare_data_loader(train_loader)
world_rank = ray.train.get_context().get_world_rank()
# Set up PyTorch Profiler for memory monitoring
with torch.profiler.profile(
activities=[
torch.profiler.ProfilerActivity.CPU,
torch.profiler.ProfilerActivity.CUDA,
],
schedule=torch.profiler.schedule(wait=0, warmup=0, active=6, repeat=1),
record_shapes=True,
profile_memory=True,
with_stack=True,
) as prof:
# Main training loop
running_loss = 0.0
num_batches = 0
epochs = config.get('epochs', 5)
for epoch in range(start_epoch, epochs):
# Set epoch for distributed sampler to ensure proper shuffling
if ray.train.get_context().get_world_size() > 1:
train_loader.sampler.set_epoch(epoch)
for images, labels in train_loader:
# Note: prepare_data_loader automatically moves data to the correct device
outputs = model(images)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
# Standard training step
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# Update profiler
prof.step()
# Track metrics
running_loss += loss.item()
num_batches += 1
# Report metrics and save checkpoint after each epoch
avg_loss = running_loss / num_batches
metrics = {"loss": avg_loss}
report_metrics_and_save_fsdp_checkpoint(model, optimizer, metrics, epoch)
# Log metrics from rank 0 only to avoid duplicate outputs
if world_rank == 0:
logger.info(metrics)
# Export memory profiling results to cluster storage
run_name = ray.train.get_context().get_experiment_name()
prof.export_memory_timeline(
f"/mnt/cluster_storage/{run_name}/rank{world_rank}_memory_profile.html"
)
# Save the final model for inference
save_model_for_inference(model, world_rank)
存储配置#
此演示使用集群存储进行快速迭代和开发,但这可能不适合生产环境或大规模部署。在这些情况下,您应该使用对象存储。有关如何选择存储类型的更多信息,请参阅 Anyscale 存储配置文档。
3. 使用 FSDP2 进行模型切分#
PyTorch 的 fully_shard 支持在各种粒度上进行切分。在最细粒度级别上,您可以切分每个层以最大限度地减少峰值内存使用率,但这也会增加 Ray Train 工作进程之间的通信成本。尝试不同的切分粒度以找到适合您用例的最佳平衡点。本示例仅切分了 encoder blocks—Vision Transformer 中最大的层。
除了切分粒度之外,FSDP2 还提供了多种配置选项来优化性能和缓解 OOM 错误
设备网格配置#
init_device_mesh 配置一个 DeviceMesh,它描述了训练运行的设备拓扑。本示例使用了简单的 1D 网格进行数据并行,但 DeviceMesh 也支持多维并行方法,包括张量并行和流水线并行。在许多情况下,集成多种并行方法可以进一步帮助提高训练性能。
有关高级多维并行配置的更多信息,请参阅 PyTorch 设备网格文档。
CPU 卸载#
CPU 卸载通过将模型组件存储在 CPU 中来减少 GPU 内存占用。但这会带来在计算过程中 CPU 和 GPU 之间数据传输开销增加的权衡。
CPU 卸载执行以下操作:
将切分后的参数、梯度和优化器状态存储在 CPU 上
在正向/反向计算期间将切分后的参数复制到 GPU,并在使用后释放
将计算出的梯度复制到 CPU,然后在 CPU 上进行优化器步进计算
何时使用 CPU 卸载
当 GPU 内存受限时
对于无法放入 GPU 内存的超大型模型
在以下情况下不要使用 CPU 卸载
当 CPU 内存有限时(可能导致 CPU 因内存不足而崩溃)
当训练速度比内存使用更重要时
无 CPU 卸载
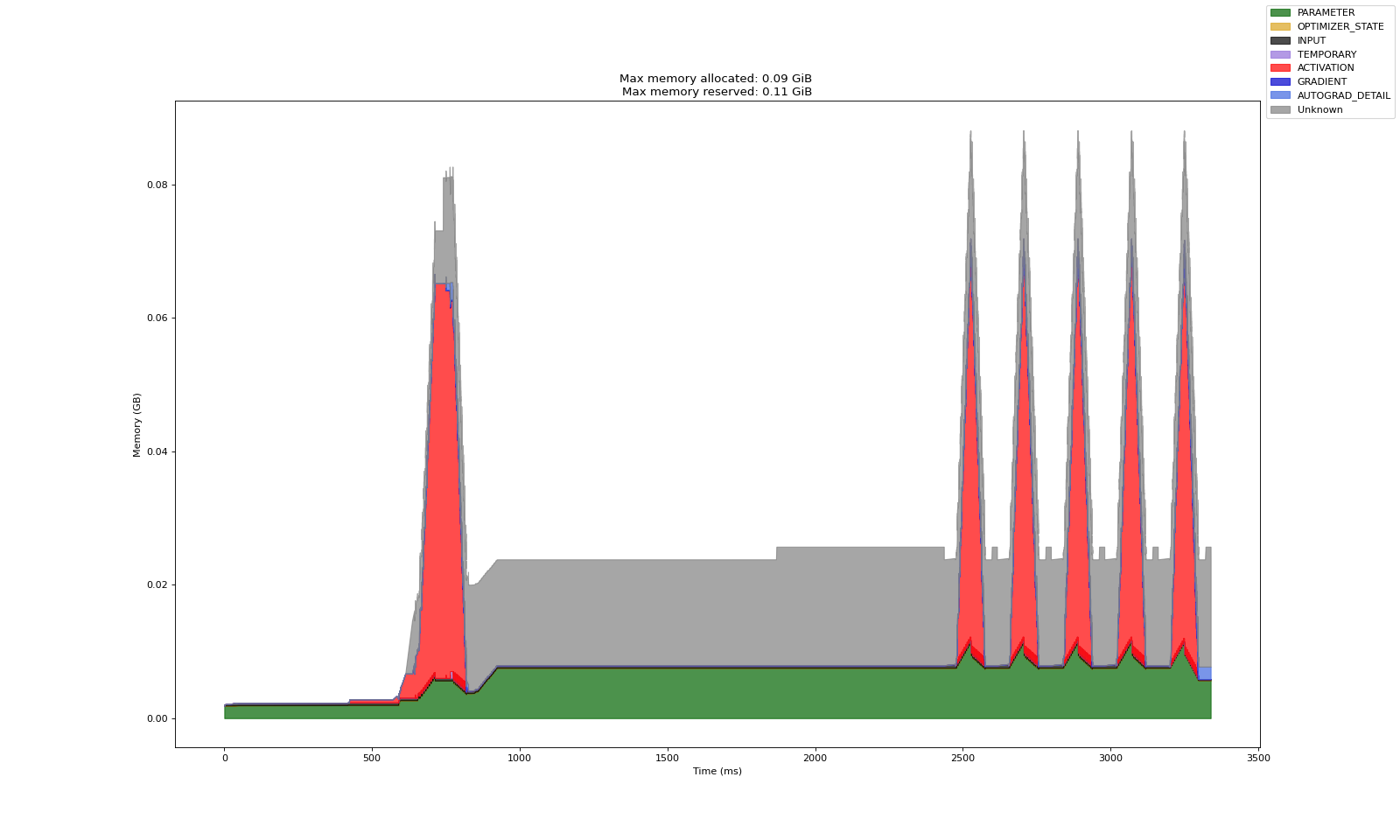
有 CPU 卸载
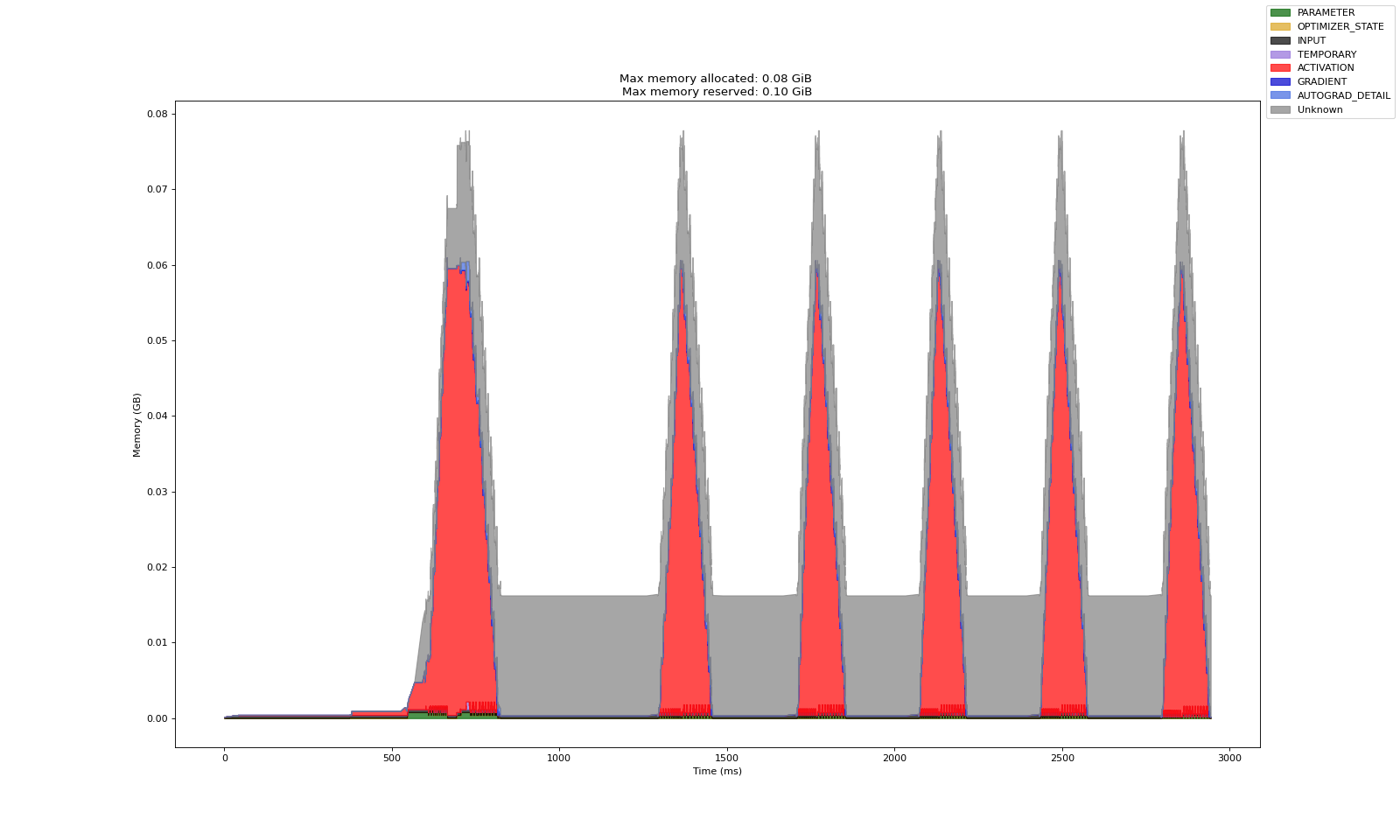
可以看到,CPU 卸载显著减少了模型参数占用的 GPU 内存量。
在 PyTorch 文档 中了解有关 CPU 卸载的更多信息。
reshard_after_forward 标志#
fully_shard 有一个 reshard_after_forward 标志,它允许在正向传播后立即释放所有收集的模型权重。这会减少峰值 GPU 内存使用率,但会增加反向传播期间工作进程之间的通信开销,因为参数需要再次全部收集。如果未切分模型参数能够完全放入每个工作进程且不构成内存瓶颈,则无需启用 reshard_after_forward。
reshard_after_forward=False

reshard_after_forward=True
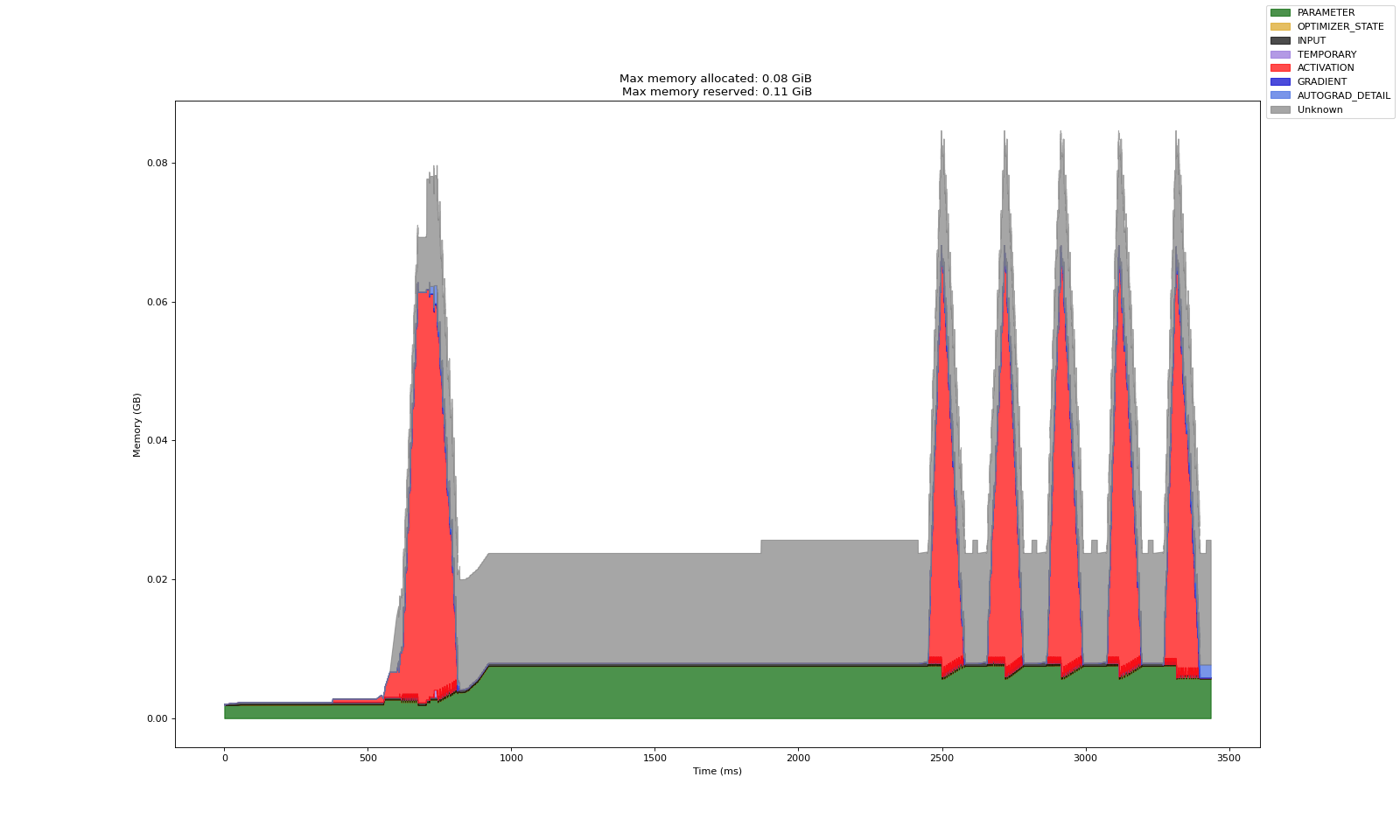
当 reshard_after_forward=True 时,模型参数占用的内存会在正向传播后下降,而在 reshard_after_forward=False 时会达到峰值。
混合精度#
启用混合精度可以加速训练并减少 GPU 内存使用,同时对精度的影响很小。
使用 FSDP2 进行混合精度的优势
减少激活和中间计算的内存使用
在现代 GPU 上实现更快的计算
通过选择性精度保持数值稳定性
无混合精度

有混合精度
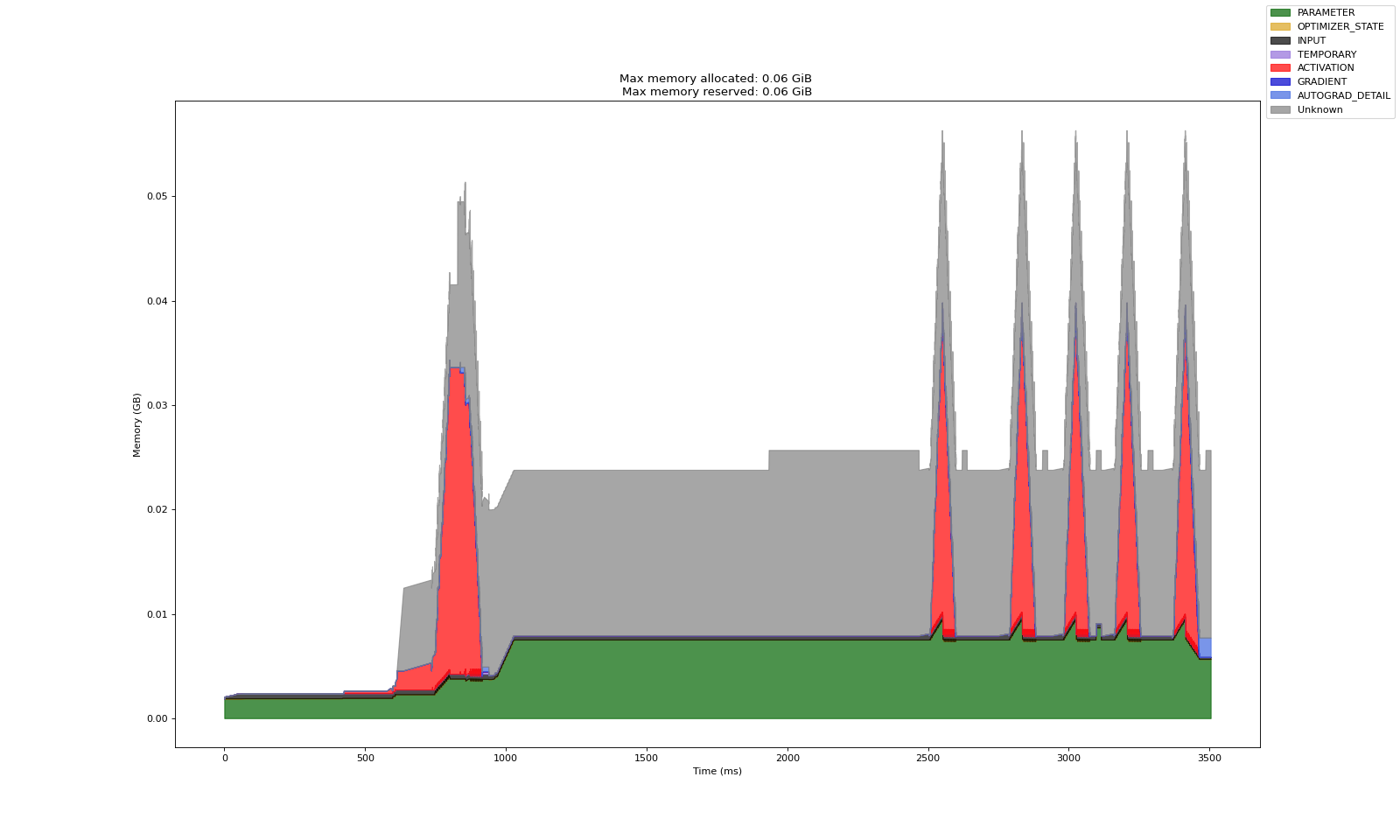
启用混合精度后,激活的峰值内存占用减半。
在 PyTorch 文档 中了解有关混合精度配置的更多信息。
组合内存策略#
下图比较了默认切分的 GPU 内存配置文件与启用了所有上述策略(CPU 卸载、混合精度、reshard_after_forward=True)时的配置文件。
默认切分

组合了 CPU 卸载、混合精度和重切分
# FSDP2 sharding imports
from torch.distributed.fsdp import (
fully_shard,
FSDPModule,
CPUOffloadPolicy,
MixedPrecisionPolicy,
)
from torch.distributed.device_mesh import init_device_mesh
def shard_model(model: torch.nn.Module):
"""Apply FSDP2 sharding to the model with optimized configuration.
Args:
model: The PyTorch model to shard
"""
logger.info("Applying FSDP2 sharding to model...")
# Step 1: Create 1D device mesh for data parallel sharding
world_size = ray.train.get_context().get_world_size()
mesh = init_device_mesh(
device_type="cuda",
mesh_shape=(world_size,),
mesh_dim_names=("data_parallel",)
)
# Step 2: Configure CPU offloading policy (optional)
offload_policy = CPUOffloadPolicy()
# Step 3: Configure mixed precision policy (optional)
mp_policy = MixedPrecisionPolicy(
param_dtype=torch.float16, # Store parameters in half precision
reduce_dtype=torch.float16, # Use half precision for gradient reduction
)
# Step 4: Apply sharding to each transformer encoder block
for encoder_block in model.encoder.layers.children():
fully_shard(
encoder_block,
mesh=mesh,
reshard_after_forward=True, # Free memory after forward pass
offload_policy=offload_policy,
mp_policy=mp_policy
)
# Step 5: Apply sharding to the root model
# This wraps the entire model and enables top-level FSDP2 functionality
fully_shard(
model,
mesh=mesh,
reshard_after_forward=True, # Free memory after forward pass
offload_policy=offload_policy,
mp_policy=mp_policy
)
4. 分布式检查点#
本节设置分布式检查点,从检查点加载分布式模型,保存分布式模型检查点,并保存用于推理的模型。
分布式检查点包装器设置#
本节使用 PyTorch 的 Stateful API 创建一个检查点包装器,以简化分布式检查点管理。根据 PyTorch 文档,这个基本包装器处理了在多个工作进程之间保存和加载 FSDP2 模型状态的复杂性。
# PyTorch Distributed Checkpoint (DCP) imports
from torch.distributed.checkpoint.state_dict import (
get_state_dict,
set_state_dict,
get_model_state_dict,
StateDictOptions
)
from torch.distributed.checkpoint.stateful import Stateful
class AppState(Stateful):
"""This is a useful wrapper for checkpointing the Application State. Because this object is compliant
with the Stateful protocol, PyTorch DCP automatically calls state_dict/load_state_dict as needed in the
dcp.save/load APIs.
Note: This wrapper is used to handle calling distributed state dict methods on the model
and optimizer.
"""
def __init__(self, model, optimizer=None, epoch=None):
self.model = model
self.optimizer = optimizer
self.epoch = epoch
def state_dict(self):
# this line automatically manages FSDP2 FQN's (Fully Qualified Name), as well as sets the default state dict type to FSDP.SHARDED_STATE_DICT
model_state_dict, optimizer_state_dict = get_state_dict(self.model, self.optimizer)
return {
"model": model_state_dict,
"optim": optimizer_state_dict,
"epoch": self.epoch
}
def load_state_dict(self, state_dict):
# sets our state dicts on the model and optimizer, now that loading is complete
set_state_dict(
self.model,
self.optimizer,
model_state_dict=state_dict["model"],
optim_state_dict=state_dict["optim"],
)
# Load epoch information if available
if "epoch" in state_dict:
self.epoch = state_dict["epoch"]
从检查点加载分布式模型#
使用 dcp.load 加载分布式检查点,它会自动处理在训练运行之间更改工作进程数量时的重切分。这种灵活性允许您在不同的资源配置下恢复训练。
# PyTorch Distributed Checkpoint (DCP) Core import
import torch.distributed.checkpoint as dcp
def load_fsdp_checkpoint(model: FSDPModule, optimizer: torch.optim.Optimizer, ckpt: ray.train.Checkpoint) -> int | None:
"""Load an FSDP checkpoint into the model and optimizer.
This function handles distributed checkpoint loading with automatic resharding
support. It can restore checkpoints even when the number of workers differs
from the original training run.
Args:
model: The FSDP-wrapped model to load state into
optimizer: The optimizer to load state into
ckpt: Ray Train checkpoint containing the saved state
Returns:
int: The epoch number saved within the checkpoint.
"""
logger.info("Loading distributed checkpoint for resuming training...")
try:
with ckpt.as_directory() as checkpoint_dir:
# Create state wrapper for DCP loading
app_state = AppState(model, optimizer)
state_dict = {"app": app_state}
# Load the distributed checkpoint
dcp.load(
state_dict=state_dict,
checkpoint_id=checkpoint_dir
)
logger.info(f"Successfully loaded distributed checkpoint from epoch {app_state.epoch}")
return app_state.epoch
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Failed to load checkpoint: {e}")
raise RuntimeError(f"Checkpoint loading failed: {e}") from e
保存模型检查点#
以下函数处理训练期间的周期性检查点保存,将指标报告与分布式检查点存储相结合
def report_metrics_and_save_fsdp_checkpoint(
model: FSDPModule, optimizer: torch.optim.Optimizer, metrics: dict, epoch: int = 0
) -> None:
"""Report training metrics and save an FSDP checkpoint.
This function performs two critical operations:
1. Saves the current model and optimizer state using distributed checkpointing
2. Reports metrics to Ray Train for tracking
Args:
model: The FSDP-wrapped model to checkpoint
optimizer: The optimizer to checkpoint
metrics: Dictionary of metrics to report (e.g., loss, accuracy)
epoch: The current epoch to be saved
"""
logger.info("Saving checkpoint and reporting metrics...")
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as temp_checkpoint_dir:
# Perform a distributed checkpoint with DCP
state_dict = {"app": AppState(model, optimizer, epoch)}
dcp.save(state_dict=state_dict, checkpoint_id=temp_checkpoint_dir)
# Report each checkpoint shard from all workers
# This saves the checkpoint to shared cluster storage for persistence
checkpoint = ray.train.Checkpoint.from_directory(temp_checkpoint_dir)
ray.train.report(metrics, checkpoint=checkpoint)
logger.info(f"Checkpoint saved successfully. Metrics: {metrics}")
保存模型以供推理#
训练后,通常需要将切分后的检查点合并到一个文件中,以便于共享或推理。与常规分布式检查点不同,此过程会生成一个与 torch.load 兼容的大型文件。为此,get_model_state_dict 函数会将参数分片全部收集到 rank 0,重建完整的 state dict,然后将合并后的检查点保存到集群存储。
请注意,此方法的关键限制是整个模型必须在 rank 0 上实例化到内存中。对于大型模型,这可能会超出可用的 CPU RAM 并导致内存不足错误。在这种情况下,建议将模型保留在其切分格式下,并依赖分布式模型加载进行推理。
def save_model_for_inference(model: FSDPModule, world_rank: int) -> None:
"""Save the complete unsharded model for inference.
This function consolidates the distributed model weights into a single
checkpoint file that can be used for inference without FSDP.
Args:
model: The FSDP2-wrapped model to save
world_rank: The rank of the current worker
"""
logger.info("Preparing model for inference...")
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as temp_checkpoint_dir:
save_file = os.path.join(temp_checkpoint_dir, "full-model.pt")
# Step 1: All-gather the model state across all ranks
# This reconstructs the complete model from distributed shards
model_state_dict = get_model_state_dict(
model=model,
options=StateDictOptions(
full_state_dict=True, # Reconstruct full model
cpu_offload=True, # Move to CPU to save GPU memory
)
)
logger.info("Successfully retrieved complete model state dict")
checkpoint = None
# Step 2: Save the complete model (rank 0 only)
if world_rank == 0:
torch.save(model_state_dict, save_file)
logger.info(f"Saved complete model to {save_file}")
# Create checkpoint for shared storage
checkpoint = ray.train.Checkpoint.from_directory(temp_checkpoint_dir)
# Step 3: Report the final checkpoint to Ray Train
ray.train.report(
{},
checkpoint=checkpoint,
checkpoint_dir_name="full_model"
)
启动分布式训练作业#
本节使用 Ray Train 的 TorchTrainer 配置并启动分布式训练作业
# Configure distributed training resources
scaling_config = ray.train.ScalingConfig(
num_workers=2, # Number of distributed workers
use_gpu=True # Enable GPU training
)
# Configure training parameters
train_loop_config = {
"epochs": 5,
"learning_rate": 0.001,
"batch_size": 64,
}
# Create experiment name
experiment_name=f"fsdp_mnist_{uuid.uuid4().hex[:8]}"
# Configure run settings and storage
run_config = ray.train.RunConfig(
# Persistent storage path accessible across all worker nodes
storage_path="/mnt/cluster_storage/",
# Unique experiment name (use consistent name to resume from checkpoints)
name=experiment_name,
# Fault tolerance configuration
failure_config=ray.train.FailureConfig(max_failures=1),
)
# Initialize and launch the distributed training job
trainer = ray.train.torch.TorchTrainer(
train_loop_per_worker=train_func,
scaling_config=scaling_config,
train_loop_config=train_loop_config,
run_config=run_config,
)
print("Starting FSDP2 training job...")
result = trainer.fit()
print("Training completed successfully!")
GPU 内存分析#
GPU 内存分析是在模型训练期间监控和分析内存使用情况的有用工具。它有助于识别瓶颈、优化资源分配并防止 OOM 错误。PyTorch 的 GPU 内存分析器在训练函数中进行配置。
在此演示中,分析器配置为为主工作进程生成一个分析文件,该文件可从集群存储的 Anyscale Files 选项卡中访问。要检查工作进程的内存配置文件,请下载相应的 HTML 文件并在浏览器中打开。分析器配置和导出路径可以在训练函数中自定义。有关 PyTorch 内存分析器的更多详细信息,请参阅 PyTorch 博客。
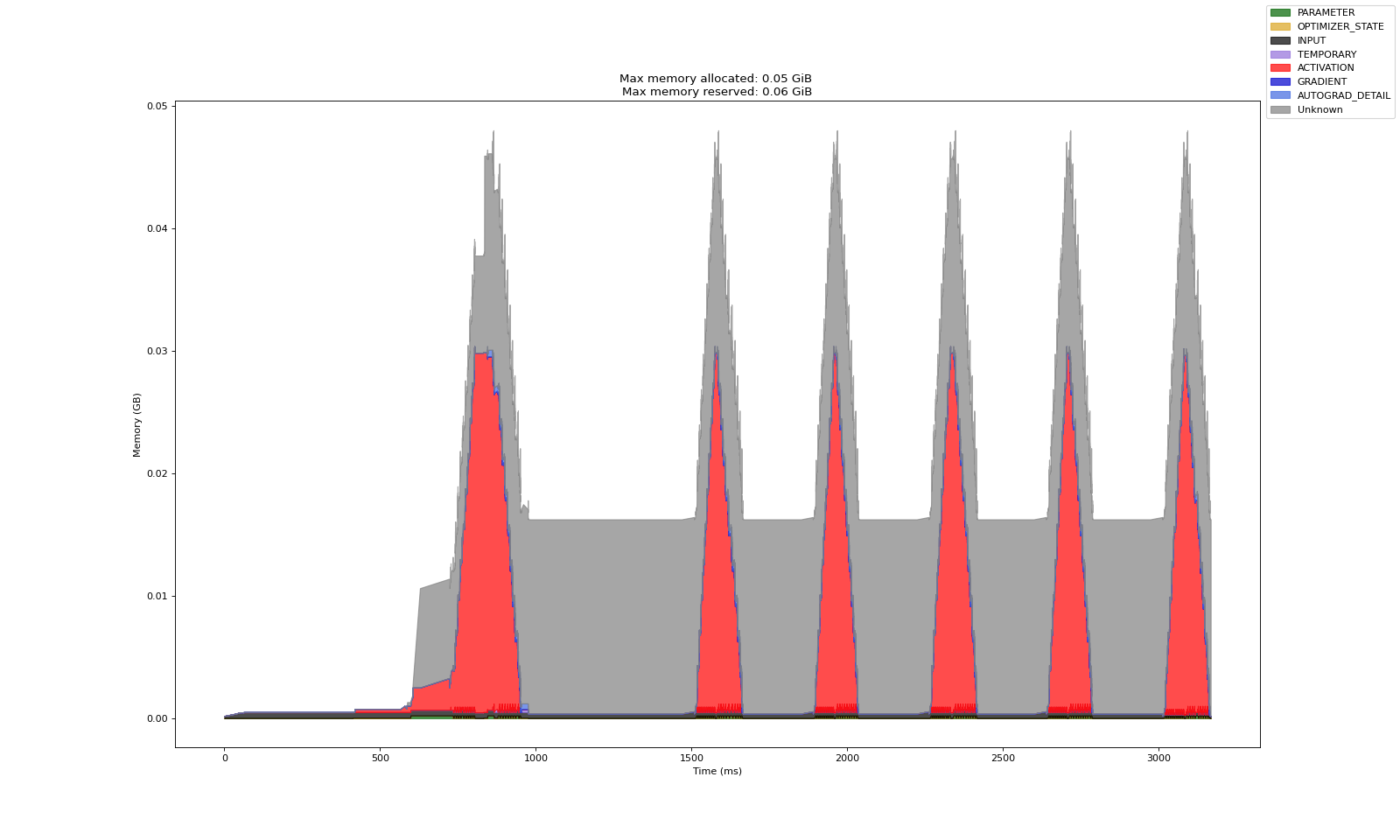
内存分析示例

训练后目录视图#
Anyscale 平台会将检查点分片、完整模型和内存分析报告保存在集群存储中,布局如下:
/mnt/cluster_storage/fsdp_mnist_1/
├── checkpoint_1/
│ ├── __0_0.distcp # Shard file for rank 0
│ └── __1_0.distcp # Shard file for rank 1
├── checkpoint_2/
│ └── ... (similar structure)
├── checkpoint_3/
│ └── ... (similar structure)
├── ... # Additional checkpoints
├── full_model/
│ └── full_model.pt # Full model checkpoint (for inference/deployment)
├── checkpoint_manager_snapshot.json
├── rank0_memory_profile.html # Memory profiling for rank 0
└── rank1_memory_profile.html # Memory profiling for rank 1
加载训练好的模型以进行推理#
训练完成后,您可以加载保存的模型以对新数据进行推理。Ray Train 以未切分的形式加载模型,准备进行标准的 PyTorch 推理。
# Update this path to match your trained model location
# The path follows the pattern: /mnt/cluster_storage/{experiment_name}/full_model/full-model.pt
PATH_TO_FULL_MODEL = f"/mnt/cluster_storage/{experiment_name}/full_model/full-model.pt"
# Initialize the same model architecture for inference
model = init_model()
# Load the trained weights
state_dict = torch.load(PATH_TO_FULL_MODEL, map_location='cpu')
model.load_state_dict(state_dict)
model.eval()
# Load the test data
transform = Compose([ToTensor(), Normalize((0.5,), (0.5,))])
test_data = FashionMNIST(
root=".", train=False, download=True, transform=transform
)
test_data
# Test model inference
with torch.no_grad():
out = model(test_data.data[0].reshape(1, 1, 28, 28).float())
predicted_label = out.argmax().item()
test_label = test_data.targets[0].item()
print(f"{predicted_label=} {test_label=}")
predicted_label=8 test_label=9
总结#
在本教程中,您执行了以下操作:
使用 FSDP2 和 Ray Train 训练了一个图像分类模型
学习了如何使用 PyTorch DCP 加载和保存分布式检查点
了解了如何配置 FSDP2 以平衡训练性能和内存使用
使用 PyTorch Memory Profiler 解锁了多 GPU 内存可观测性