构建一个常规的 RAG 文档摄取管道(无需 Ray)#
引言#
在本教程中,我们将构建一个完成以下任务的文档处理管道:
使用 Unstructured IO 加载各种文档格式(PDF、DOCX、PPTX、HTML、TXT)。
应用文本分块策略(固定和递归)来分解文本以供进一步处理。
使用嵌入模型嵌入文本块。
将嵌入存储到 Chroma DB 中,以实现进一步的文档检索功能。
这是架构图
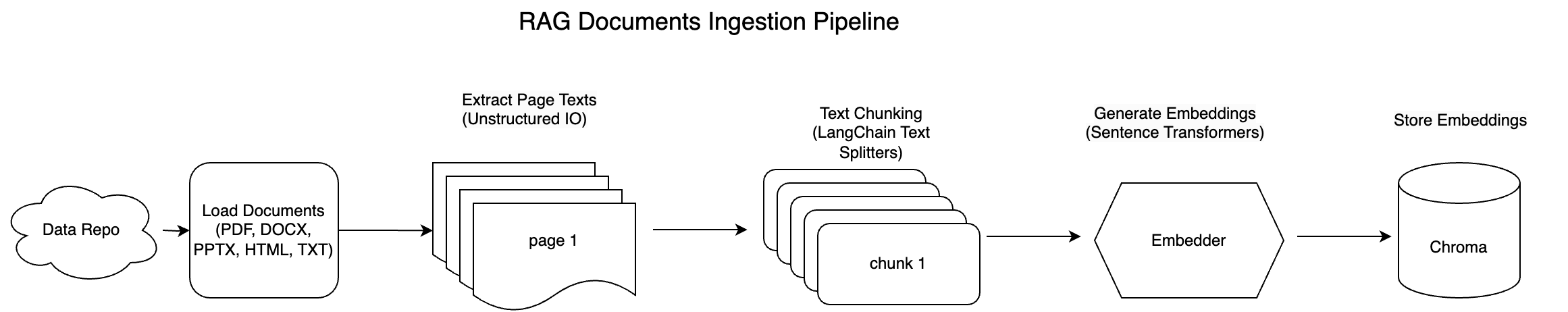
此管道旨在为下游任务准备您的数据,同时确保处理各种文档类型的灵活性和有效性。
本教程不需要 RAY — 只需熟悉构建 RAG 和非结构化文档摄取即可。如果您已经熟悉 RAG 文档摄取过程,可以跳过本教程。
在 Notebook #2 中,我们将更详细地介绍如何使用 Ray 来扩展此过程以进行大规模文档处理。
注意:本教程针对 Anyscale 平台进行了优化。在开源 Ray 上运行时,需要额外的配置。例如,您需要手动
- 配置您的 Ray 集群:设置您的多节点环境(包括主节点和工作节点),并管理资源分配(例如,自动伸缩、GPU/CPU 分配),而无需 Anyscale 的自动化。有关详细信息,请参阅 Ray 集群设置文档:https://docs.rayai.org.cn/en/latest/cluster/getting-started.html。
- 管理依赖项:在每个节点上安装和管理依赖项,因为您将无法使用 Anyscale 基于 Docker 的依赖项管理。请参阅 Ray 安装指南,了解在环境中安装和更新 Ray 的说明:https://docs.rayai.org.cn/en/latest/ray-core/handling-dependencies.html。
- 设置存储:配置您自己的分布式或共享存储系统(而不是依赖 Anyscale 的集成集群存储)。请查看 Ray 集群配置指南,了解有关设置共享存储解决方案的建议:https://docs.rayai.org.cn/en/latest/train/user-guides/persistent-storage.html。
使用 Unstructured IO 加载文档#
在工作区中,名为 anyscale-jobs-docs 的文件夹包含 5 份不同格式的文档,包括 PDF、PPTX、HTML、TXT 和 DOCX。
我们定义了一个函数,使用 Unstructured IO 库进行解析来加载和分区这些文档。更多信息请访问:https://docs.unstructured.io/welcome。
文档从指定目录读取,并按页面进行处理。每个页面的文本与其相应的元数据一起分组 — 例如源文件详细信息、文件类型、页码和唯一文档 ID。
import os
import re
from typing import List, Dict
from pathlib import Path
import uuid
# Importing our document partitioner from unstructured.io
from unstructured.partition.auto import partition
def process_documents_pages(source_dir: str) -> List[Dict]:
"""
Load documents from a given directory using Unstructured IO and group text by page number.
Args:
source_dir (str): Directory containing documents.
Returns:
List[Dict]: A list of dictionaries where each dictionary contains:
- 'text': combined text from a page,
- 'source': file path,
- 'file_name': file name with extension,
- 'file_type': file extension,
- 'page_number': page number,
- 'doc_id': a unique id for the entire file.
"""
pages = []
for file_path in Path(source_dir).rglob('*'):
if file_path.suffix.lower() in ('.pdf', '.docx', '.pptx', '.html', '.txt'):
print("processing file:", file_path)
elements = partition(str(file_path))
doc_id = str(uuid.uuid4()) # Single doc_id per file
# Group text by page number
page_texts = {}
for el in elements:
# Get the page number; default to 1 if not provided
page_number = getattr(el.metadata, "page_number", None)
page_number = int(page_number) if page_number is not None else 1
# Append element text to the corresponding page's list
page_texts.setdefault(page_number, []).append(str(el))
# Create a document entry for each page
for page_number, texts in page_texts.items():
combined_text = " ".join(texts).strip()
pages.append({
"text": combined_text,
"source": str(file_path),
"file_name": file_path.name,
"file_type": file_path.suffix,
"page_number": page_number,
"doc_id": doc_id
})
return pages
source_directory = "./anyscale-jobs-docs" # Replace with your actual folder path
pages = process_documents_pages(source_directory)
for page in pages:
print(f"File Name: {page['file_name']}")
print(f"Page Number: {page['page_number']}")
print(f"Text: {page['text'][:200]}...") # Truncate text to 100 characters
print("-" * 80) # Separator for readability
processing file: anyscale-jobs-docs/Create_and_manage_jobs.pdf
processing file: anyscale-jobs-docs/Job_queues.pptx
processing file: anyscale-jobs-docs/Monitor_a_job.docx
processing file: anyscale-jobs-docs/Jobs.txt
processing file: anyscale-jobs-docs/Job_schedules.html
File Name: Create_and_manage_jobs.pdf
Page Number: 1
Text: 2/12/25, 9:48 AM Create and manage jobs | Anyscale Docs Create and manage jobs Submitting a job To submit your job to Anyscale, use the Python SDK or CLI and pass in any additional options or configur...
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
File Name: Create_and_manage_jobs.pdf
Page Number: 2
Text: 2/12/25, 9:48 AM Create and manage jobs | Anyscale Docs Defining a job With the CLI, you can define jobs in a YAML file and submit them by referencing the YAML: anyscale job submit --config-file confi...
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
File Name: Create_and_manage_jobs.pdf
Page Number: 3
Text: 2/12/25, 9:48 AM Create and manage jobs | Anyscale Docs anyscale job terminate --id 'prodjob_...' For more information on terminating jobs with the CLI, see the reference docs. Archiving a job Archivi...
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
File Name: Create_and_manage_jobs.pdf
Page Number: 4
Text: 2/12/25, 9:48 AM Create and manage jobs | Anyscale Docs 2. When submitting your job, include the -r or --requirements flag: CLI Python SDK anyscale job submit --config-file job.yaml -r ./requirements....
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
File Name: Create_and_manage_jobs.pdf
Page Number: 5
Text: 2/12/25, 9:48 AM Create and manage jobs | Anyscale Docs Using pre-built custom images For frequently used environments, you can build and reuse custom images: 1. Build the image: CLI Python SDK anysca...
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
File Name: Job_queues.pptx
Page Number: 1
Text: 2/12/25, 9:48 AM Job queues | Anyscale Docs Job queues A job queue enables sophisticated scheduling and execution algorithms for Anyscale Jobs. This feature improves resource utilization and reduces p...
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
File Name: Job_queues.pptx
Page Number: 2
Text: 2/12/25, 9:48 AM Job queues | Anyscale Docs entrypoint: python hello_world.py working_dir: "https://github.com/anyscale/docs_examples/archive/refs/heads/main.zip" name: JOB_NAME # Use compute_config a...
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
File Name: Job_queues.pptx
Page Number: 3
Text: 2/12/25, 9:48 AM config to associate with the existing queue. Job queues | Anyscale Docs The submission will fail if you submit a job with the same job queue name but a different job_queue_spec , comp...
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
File Name: Job_queues.pptx
Page Number: 4
Text: 2/12/25, 9:48 AM Job queues | Anyscale Docs To terminate all running jobs in the queue, use the Terminate running jobs button on the upper right corner of the Job queue page. Note that Anyscale doesn'...
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
File Name: Job_queues.pptx
Page Number: 5
Text: 2/12/25, 9:48 AM Job queues | Anyscale Docs Open the Terminal tab and run ray job stop 'raysubmit_...' . https://docs.anyscale.com/platform/jobs/job-queues 3/5...
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
File Name: Monitor_a_job.docx
Page Number: 1
Text: Monitor a job Anyscale jobs provides several tools to monitor your jobs: Job detail page Metrics Logs Alerts Ray Dashboard Exporting logs and metrics This document describes each use case and provides...
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
File Name: Jobs.txt
Page Number: 1
Text: 2/12/25, 9:48 AM Jobs | Anyscale Docs Jobs Run discrete workloads in production such as batch inference, bulk embeddings generation, or model fine-tuning. Anyscale Jobs allow you to submit application...
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
File Name: Job_schedules.html
Page Number: 1
Text: Create and manage jobs Submitting a job To submit your job to Anyscale, use the Python SDK or CLI and pass in any additional options or configurations for the job. By default, Anyscale uses your work...
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
分块策略#
本节演示了使用专门的文本分割器将文档分割成更小的、可管理文本块的各种策略。 ChunkingStrategy 类允许用户使用“固定”或“递归”方法将文本分割成更小的块,并具有可配置的参数,如编码类型、块大小和重叠。
## doc: https://python.langchain.ac.cn/v0.1/docs/modules/data_connection/document_transformers/
from typing import List
# Importing various text splitters for different chunking strategies
from langchain_text_splitters import (
RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter,
CharacterTextSplitter
)
class ChunkingStrategy:
def __init__(self, method: str = 'recursive', encoding_name: str = "cl100k_base",
chunk_size: int = 300, chunk_overlap: int = 50):
"""
Initialize a chunking strategy.
Args:
method (str): The chunking method, e.g. 'fixed' or 'recursive'.
encoding_name (str): The name of the encoding to use.
chunk_size (int): The size of each chunk.
chunk_overlap (int): The overlap between chunks.
"""
self.method = method
self.encoding_name = encoding_name
self.chunk_size = chunk_size
self.chunk_overlap = chunk_overlap
def chunk_document(self, text: str) -> List[str]:
"""
Chunk a document's text using the selected strategy.
Args:
text (str): The document's text to chunk.
Returns:
List[str]: A list of text chunks.
"""
if self.method == 'fixed':
splitter = CharacterTextSplitter.from_tiktoken_encoder(
encoding_name=self.encoding_name,
chunk_size=self.chunk_size,
chunk_overlap=self.chunk_overlap
)
return splitter.split_text(text)
elif self.method == 'recursive':
splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter.from_tiktoken_encoder(
encoding_name=self.encoding_name,
chunk_size=self.chunk_size,
chunk_overlap=self.chunk_overlap
)
return splitter.split_text(text)
else:
raise ValueError("Unknown chunking method: choose 'fixed' or 'recursive'.")
测试分块策略实现#
现在,让我们对单个页面应用分块过程
## Test the Chunking Strategy Implementation
# Create a ChunkingStrategy instance with the desired settings.
chunker = ChunkingStrategy(chunk_size=300, chunk_overlap=50)
# Retrieve page information from the pages list (using the 11th page as an example).
page = pages[10]
file_name = page["file_name"]
file_type = page["file_type"]
page_number = page["page_number"]
text_content = page["text"]
# Debug: Print the text content of the selected page.
print("Debug - Page Text:", text_content)
# Chunk the document text using the chunk_document method.
chunks = chunker.chunk_document(text_content)
# Display file and page details along with the number of chunks generated.
print(f"File: {file_name} (Page Number: {page_number})")
print(f"Number of chunks: {len(chunks)}")
print("-" * 80)
# Iterate through each chunk and print its contents.
for idx, chunk in enumerate(chunks):
print(f"Chunk {idx + 1}:")
print(chunk)
print("-" * 80)
Debug - Page Text: Monitor a job Anyscale jobs provides several tools to monitor your jobs: Job detail page Metrics Logs Alerts Ray Dashboard Exporting logs and metrics This document describes each use case and provides suggestions for when to use each tool. Job detail page The job detail page contains the status of the job, information about your job's configuration, details about each job attempt, events of the job, and links to various other tools. The job events log is at the bottom of the page. This log lists events of your job aAnsdkinAcIludes events about your job lifecycle and errors. Metrics Access metrics related to your job in the Metrics tab of the job detail page. Job metrics tracks hardware metrics and system-level metrics such as CPU or network utilization, memory, or disk usage, node count, number of Ray tasks, and number of active Ray actors. Metrics are also available in Grafana for a more advanced UI, which allows you to create custom dashboards for visualizing the metrics, including custom metrics. Access Grafana by clicking the View in Grafana button in the Metrics tab. Logs Logs are another source of information when debugging issues with your job. You can view the logs of your job by clicking the "Logs" tab in the job detail page. By default, you can will see the driver logs of your job. If the job is still running, you can also view the Ray logs of the job through the Ray Dashboard. Log viewer If you have enabled log ingestion, you have access to the Anyscale log viewer With the Anyscale log viewer, you have access to all Ray logs of your jobs and can search and filter by time, text, or labels such as task name, node ID, and more. By default, the logs are filtered to the time range of the job with no filters. You can change the time range by clicking the time range dropdown and select an end time and time window to look back. Anyscale stores up to 30 days of logs for your job. You're able to debug issues even after the job terminates. To filter the logs, use the search bar to search for specific keywords. Enter a request ID in the search bar to filter logs for a specific request. You can also use contain a specific pattern. Alerts to filter logs if your logs Anyscale jobs have a built-in alert for when a job succeeds or fails. The creator of the job receives an email notification when the job completes. To set up additional alerts based on your own criteria, see Custom dashboards and alerting guide. These alerts are useful for tracking the health of your jobs or job queues. Ray Dashboard The Ray Dashboard is scoped to a single Ray cluster. Each job attempt launches a new Ray cluster unless Job queues are used. To access this dashboard, click the "Ray Dashboard" tab in the job detail page. To learn more about how to use the Ray Dashboard, see the Ray documentation. Exporting logs and metrics If you want to push logs to Vector, a tool to ship logs to Amazon CloudWatch, Google Cloud Monitoring, Datadog, or other observability tools, see Exporting logs and metrics with Vector. More info To learn more details about the Ray Dashboard, see the Ray Dashboard documentation To learn more about Grafana and how to use it, see the official Grafana documentation To learn more about the metrics that Ray emits, see the System Metrics documentation
File: Monitor_a_job.docx (Page Number: 1)
Number of chunks: 3
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Chunk 1:
Monitor a job Anyscale jobs provides several tools to monitor your jobs: Job detail page Metrics Logs Alerts Ray Dashboard Exporting logs and metrics This document describes each use case and provides suggestions for when to use each tool. Job detail page The job detail page contains the status of the job, information about your job's configuration, details about each job attempt, events of the job, and links to various other tools. The job events log is at the bottom of the page. This log lists events of your job aAnsdkinAcIludes events about your job lifecycle and errors. Metrics Access metrics related to your job in the Metrics tab of the job detail page. Job metrics tracks hardware metrics and system-level metrics such as CPU or network utilization, memory, or disk usage, node count, number of Ray tasks, and number of active Ray actors. Metrics are also available in Grafana for a more advanced UI, which allows you to create custom dashboards for visualizing the metrics, including custom metrics. Access Grafana by clicking the View in Grafana button in the Metrics tab. Logs Logs are another source of information when debugging issues with your job. You can view the logs of your job by clicking the "Logs" tab in the job detail page. By default, you can will see the driver logs of your job. If the job is still running, you can also view the Ray logs of the job through the Ray Dashboard. Log viewer If you have enabled log ingestion, you have access
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Chunk 2:
page. By default, you can will see the driver logs of your job. If the job is still running, you can also view the Ray logs of the job through the Ray Dashboard. Log viewer If you have enabled log ingestion, you have access to the Anyscale log viewer With the Anyscale log viewer, you have access to all Ray logs of your jobs and can search and filter by time, text, or labels such as task name, node ID, and more. By default, the logs are filtered to the time range of the job with no filters. You can change the time range by clicking the time range dropdown and select an end time and time window to look back. Anyscale stores up to 30 days of logs for your job. You're able to debug issues even after the job terminates. To filter the logs, use the search bar to search for specific keywords. Enter a request ID in the search bar to filter logs for a specific request. You can also use contain a specific pattern. Alerts to filter logs if your logs Anyscale jobs have a built-in alert for when a job succeeds or fails. The creator of the job receives an email notification when the job completes. To set up additional alerts based on your own criteria, see Custom dashboards and alerting guide. These alerts are useful for tracking the health of your jobs or job queues. Ray Dashboard The Ray Dashboard is scoped to a single Ray cluster. Each job attempt launches a new Ray cluster unless Job queues
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Chunk 3:
criteria, see Custom dashboards and alerting guide. These alerts are useful for tracking the health of your jobs or job queues. Ray Dashboard The Ray Dashboard is scoped to a single Ray cluster. Each job attempt launches a new Ray cluster unless Job queues are used. To access this dashboard, click the "Ray Dashboard" tab in the job detail page. To learn more about how to use the Ray Dashboard, see the Ray documentation. Exporting logs and metrics If you want to push logs to Vector, a tool to ship logs to Amazon CloudWatch, Google Cloud Monitoring, Datadog, or other observability tools, see Exporting logs and metrics with Vector. More info To learn more details about the Ray Dashboard, see the Ray Dashboard documentation To learn more about Grafana and how to use it, see the official Grafana documentation To learn more about the metrics that Ray emits, see the System Metrics documentation
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
现在,让我们对所有文档进行分块,并收集块及其元数据
import uuid
all_chunks = []
for page in pages:
chunks = chunker.chunk_document(page["text"])
for chunk in chunks:
all_chunks.append({
"id": str(uuid.uuid4()), # Generate a unique ID for each chunk
"text": chunk,
"metadata": {
"source": page["source"],
"doc_id": page["doc_id"],
"file_name": page["file_name"],
"file_type": page["file_type"],
"page_number": page["page_number"],
"chunk_method": chunker.method
}
})
print(f"Created {len(all_chunks)} text chunks.")
Created 22 text chunks.
生成嵌入#
在设置 Chroma DB 以进行向量存储之前,请先为文本块生成嵌入。我们使用的是 intfloat/multilingual-e5-large-instruct 模型。
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer
# Initialize a SentenceTransformer model (choose one appropriate for your use case)
embed_model = SentenceTransformer("intfloat/multilingual-e5-large-instruct")
# Gather all chunk texts for embedding generation
chunk_texts = [chunk["text"] for chunk in all_chunks]
# Compute embeddings (using batch encoding for efficiency)
embeddings = embed_model.encode(chunk_texts, convert_to_numpy=True, show_progress_bar=True)
# Attach each embedding (converted to a list) to the corresponding chunk
for i, chunk in enumerate(all_chunks):
chunk["embedding"] = embeddings[i].tolist()
print("Embeddings generated and attached to each chunk.")
Embeddings generated and attached to each chunk.
设置 Chroma DB#
我们使用 ChromaDB 来存储和管理我们计算出的嵌入。出于演示目的,初始化了一个临时目录用于持久存储,并创建了一个 ChromaDB 客户端以及一个名为“sample_embeddings”的集合,用于存储嵌入、相关元数据和文档文本。
import tempfile
import chromadb
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer
# Create a temporary directory
temp_dir = tempfile.TemporaryDirectory()
temp_chroma_db_path = temp_dir.name # This is the path for ChromaDB storage
# Initialize ChromaDB client
chroma_client = chromadb.PersistentClient(path=temp_chroma_db_path) # Change path as needed
collection = chroma_client.get_or_create_collection(name="sample_embeddings")
# Store embeddings in ChromaDB
collection.add(
ids=[chunk["id"] for chunk in all_chunks],
embeddings=embeddings.tolist(),
metadatas=[chunk["metadata"] for chunk in all_chunks],
documents=chunk_texts
)
print("Embeddings stored in ChromaDB.")
Embeddings stored in ChromaDB.
使用 Chroma 进行嵌入搜索#
我们对存储在 ChromaDB 中的相关文档嵌入执行搜索。通过为给定的文本查询生成一个嵌入,我们可以识别并检索集合中最相似的文档,以及它们的元数据和相似度得分。
from pprint import pprint
# Define your text query
query_text = "how to submit anyscale jobs"
# Generate the embedding for the query text
query_embedding = embed_model.encode(query_text).tolist()
# Query the collection for the top 3 most similar documents.
# The 'include' parameter lets you retrieve documents, metadatas, and distances.
results = collection.query(
query_embeddings=[query_embedding],
n_results=3,
include=["documents", "metadatas", "distances"]
)
# Print the retrieval results
print("Query Results:")
pprint(results)
Query Results:
{'data': None,
'distances': [[0.18700521448677737, 0.18982562470474848, 0.1924720483496574]],
'documents': [['Create and manage jobs Submitting a job\u200b To submit your '
'job to Anyscale, use the Python SDK or CLI and pass in any '
'additional options or configurations for the job. By default, '
'Anyscale uses your workspace or cloud to provision a cluster '
'to run your job. You can define a custom cluster through a '
'compute config or specify an existing cluster. Once '
'submitted, Anyscale runs the job as specified in the '
'entrypoint command, which is typically a Ray Job. If the run '
"doesn't succeed, the job restarts using the same entrypoint "
'up to the number of max_retries. CLI Python SDK anyscale job '
'submit --name=my-job \\\n'
' --working-dir=. --max-retries=5 \\\n'
' --image-uri="anyscale/image/IMAGE_NAME:VERSION" \\\n'
' --compute-config=COMPUTE_CONFIG_NAME \\\n'
' -- python main.py With the CLI, you can either specify an '
'existing compute config with '
'--compute-config=COMPUTE_CONFIG_NAME or define a new one in a '
'job YAML. For more information on submitting jobs with the '
'CLI, see the reference docs. import anyscale\n'
'from anyscale.job.models import JobConfig\n'
'\n'
'config = JobConfig(\n'
' name="my-job",\n'
' entrypoint="python main.py",\n'
' working_dir=".",\n'
' max_retries=5,\n'
' image_uri="anyscale/image/IMAGE_NAME:VERSION",\n'
' compute_config="COMPUTE_CONFIG_NAME"\n'
')',
'2/12/25, 9:48 AM Create and manage jobs | Anyscale Docs '
'Create and manage jobs Submitting a job To submit your job to '
'Anyscale, use the Python SDK or CLI and pass in any '
'additional options or configurations for the job. By default, '
'Anyscale uses your workspace or cloud to provision a cluster '
'to run your job. You can define a custom cluster through a '
'compute config or specify an existing cluster. Once '
'submitted, Anyscale runs the job as specified in the '
'entrypoint command, which is typically a Ray Job. If the run '
"doesn't succeed, the job restarts using the same entrypoint "
'up to the number of max_retries . CLI Python SDK anyscale job '
'submit --name=my-job \\ --working-dir=. --max-retries=5 \\ '
'--image-uri="anyscale/image/IMAGE_NAME:VERSION" \\ '
'--compute-config=COMPUTE_CONFIG_NAME \\ -- python main.py '
'With the CLI, you can either specify an existing compute '
'config with --compute- config=COMPUTE_CONFIG_NAME or define a '
'new one in a job YAML. For more information on submitting '
'jobs with the CLI, see the reference docs. TIP For '
'large-scale, compute-intensive jobs, avoid scheduling Ray '
'tasks onto the head node because it manages cluster-level '
'orchestration. To do that, set the CPU resource on the head '
'node to 0 in your compute config. Ask AI '
'https://docs.anyscale.com/platform/jobs/manage-jobs 1/5',
'2/12/25, 9:48 AM Jobs | Anyscale Docs Jobs Run discrete '
'workloads in production such as batch inference, bulk '
'embeddings generation, or model fine-tuning. Anyscale Jobs '
'allow you to submit applications developed on workspaces to a '
'standalone Ray cluster for execution. Built for production '
'and designed to fit into your CI/CD pipeline, jobs ensure '
'scalable and reliable performance. How does it work? # When '
'you’re ready to promote an app to production, submit a job '
'from the workspace using anyscale job submit . Anyscale Jobs '
'have the following features: Scalability: Rapid scaling to '
'thousands of cloud instances, adjusting computing resources '
'to match application demand. Fault tolerance: Retries for '
'failures and automatic rescheduling to an alternative cluster '
'for unexpected failures like running out of memory. '
'Monitoring and observability: Persistent dashboards that '
'allow you to observe tasks in real time and email alerts upon '
'successf ul job completion. Get started 1. Sign in or sign up '
'for an account. 2. Select the Intro to Jobs example. 3. '
'Select Launch. This example runs in a Workspace. See '
'Workspaces for background information. 4. Follow the notebook '
'or view it in the docs. 5. Terminate the Workspace when '
"you're done. Ask AI https://docs.anyscale.com/platform/jobs/ "
'1/2 2/12/25, 9:48 AM Jobs | Anyscale Docs '
'https://docs.anyscale.com/platform/jobs/']],
'embeddings': None,
'ids': [['d972e888-9aa4-4e8c-9543-ece3b21ab2f3',
'19a58587-1fe6-43c8-8275-be2755a0f8a1',
'c2bfae32-ea87-47dd-97b3-9a55ad2585d6']],
'included': [<IncludeEnum.distances: 'distances'>,
<IncludeEnum.documents: 'documents'>,
<IncludeEnum.metadatas: 'metadatas'>],
'metadatas': [[{'chunk_method': 'recursive',
'doc_id': 'fc073a75-025a-4b5e-8192-7a3a73f92739',
'file_name': 'Job_schedules.html',
'file_type': '.html',
'page_number': 1,
'source': 'anyscale-jobs-docs/Job_schedules.html'},
{'chunk_method': 'recursive',
'doc_id': '9ee4e77b-8ff9-4ea9-afc6-e67642798174',
'file_name': 'Create_and_manage_jobs.pdf',
'file_type': '.pdf',
'page_number': 1,
'source': 'anyscale-jobs-docs/Create_and_manage_jobs.pdf'},
{'chunk_method': 'recursive',
'doc_id': 'c87a8846-5a60-4e95-9805-fe1dce18507c',
'file_name': 'Jobs.txt',
'file_type': '.txt',
'page_number': 1,
'source': 'anyscale-jobs-docs/Jobs.txt'}]],
'uris': None}
重新格式化 Chroma 搜索结果#
从 Chroma 返回的嵌入搜索结果不直观,因此让我们重新格式化它们。
from pprint import pprint
def reformat(chroma_results: dict) -> list:
"""
Reformat chroma db results to a list of search items containing:
- chunk_id
- chunk_index
- doc_id
- page_number
- source
- text (from documents)
- distance
- score
Parameters:
chroma_results (dict): The raw results from the Chroma DB query.
Returns:
list: A list of dictionaries with the desired keys.
"""
reformatted = []
# Get the lists from the results. They are expected to be lists of lists.
metadatas = chroma_results.get("metadatas", [])
documents = chroma_results.get("documents", [])
distances = chroma_results.get("distances", [])
# Loop over each group (each inner list represents one set of matches)
chunk_index = 1
for meta_group, doc_group, distance_group in zip(metadatas, documents, distances):
# Iterate over each item in the inner lists
for meta, text, distance in zip(meta_group, doc_group, distance_group):
item = {
"chunk_index": chunk_index,
"chunk_id": meta.get("chunk_id"),
"doc_id": meta.get("doc_id"),
"page_number": meta.get("page_number"),
"source": meta.get("source"),
"text": text,
"distance": distance,
"score": 1 - distance
}
reformatted.append(item)
chunk_index += 1
return reformatted
print("refromat Results:")
pprint(reformat(results))
refromat Results:
[{'chunk_id': None,
'chunk_index': 1,
'distance': 0.18700521448677737,
'doc_id': 'fc073a75-025a-4b5e-8192-7a3a73f92739',
'page_number': 1,
'score': 0.8129947855132227,
'source': 'anyscale-jobs-docs/Job_schedules.html',
'text': 'Create and manage jobs Submitting a job\u200b To submit your job to '
'Anyscale, use the Python SDK or CLI and pass in any additional '
'options or configurations for the job. By default, Anyscale uses '
'your workspace or cloud to provision a cluster to run your job. You '
'can define a custom cluster through a compute config or specify an '
'existing cluster. Once submitted, Anyscale runs the job as '
'specified in the entrypoint command, which is typically a Ray Job. '
"If the run doesn't succeed, the job restarts using the same "
'entrypoint up to the number of max_retries. CLI Python SDK anyscale '
'job submit --name=my-job \\\n'
' --working-dir=. --max-retries=5 \\\n'
' --image-uri="anyscale/image/IMAGE_NAME:VERSION" \\\n'
' --compute-config=COMPUTE_CONFIG_NAME \\\n'
' -- python main.py With the CLI, you can either specify an '
'existing compute config with --compute-config=COMPUTE_CONFIG_NAME '
'or define a new one in a job YAML. For more information on '
'submitting jobs with the CLI, see the reference docs. import '
'anyscale\n'
'from anyscale.job.models import JobConfig\n'
'\n'
'config = JobConfig(\n'
' name="my-job",\n'
' entrypoint="python main.py",\n'
' working_dir=".",\n'
' max_retries=5,\n'
' image_uri="anyscale/image/IMAGE_NAME:VERSION",\n'
' compute_config="COMPUTE_CONFIG_NAME"\n'
')'},
{'chunk_id': None,
'chunk_index': 2,
'distance': 0.18982562470474848,
'doc_id': '9ee4e77b-8ff9-4ea9-afc6-e67642798174',
'page_number': 1,
'score': 0.8101743752952515,
'source': 'anyscale-jobs-docs/Create_and_manage_jobs.pdf',
'text': '2/12/25, 9:48 AM Create and manage jobs | Anyscale Docs Create and '
'manage jobs Submitting a job To submit your job to Anyscale, use '
'the Python SDK or CLI and pass in any additional options or '
'configurations for the job. By default, Anyscale uses your '
'workspace or cloud to provision a cluster to run your job. You can '
'define a custom cluster through a compute config or specify an '
'existing cluster. Once submitted, Anyscale runs the job as '
'specified in the entrypoint command, which is typically a Ray Job. '
"If the run doesn't succeed, the job restarts using the same "
'entrypoint up to the number of max_retries . CLI Python SDK '
'anyscale job submit --name=my-job \\ --working-dir=. '
'--max-retries=5 \\ --image-uri="anyscale/image/IMAGE_NAME:VERSION" '
'\\ --compute-config=COMPUTE_CONFIG_NAME \\ -- python main.py With '
'the CLI, you can either specify an existing compute config with '
'--compute- config=COMPUTE_CONFIG_NAME or define a new one in a job '
'YAML. For more information on submitting jobs with the CLI, see the '
'reference docs. TIP For large-scale, compute-intensive jobs, avoid '
'scheduling Ray tasks onto the head node because it manages '
'cluster-level orchestration. To do that, set the CPU resource on '
'the head node to 0 in your compute config. Ask AI '
'https://docs.anyscale.com/platform/jobs/manage-jobs 1/5'},
{'chunk_id': None,
'chunk_index': 3,
'distance': 0.1924720483496574,
'doc_id': 'c87a8846-5a60-4e95-9805-fe1dce18507c',
'page_number': 1,
'score': 0.8075279516503426,
'source': 'anyscale-jobs-docs/Jobs.txt',
'text': '2/12/25, 9:48 AM Jobs | Anyscale Docs Jobs Run discrete workloads '
'in production such as batch inference, bulk embeddings generation, '
'or model fine-tuning. Anyscale Jobs allow you to submit '
'applications developed on workspaces to a standalone Ray cluster '
'for execution. Built for production and designed to fit into your '
'CI/CD pipeline, jobs ensure scalable and reliable performance. How '
'does it work? # When you’re ready to promote an app to production, '
'submit a job from the workspace using anyscale job submit . '
'Anyscale Jobs have the following features: Scalability: Rapid '
'scaling to thousands of cloud instances, adjusting computing '
'resources to match application demand. Fault tolerance: Retries for '
'failures and automatic rescheduling to an alternative cluster for '
'unexpected failures like running out of memory. Monitoring and '
'observability: Persistent dashboards that allow you to observe '
'tasks in real time and email alerts upon successf ul job '
'completion. Get started 1. Sign in or sign up for an account. 2. '
'Select the Intro to Jobs example. 3. Select Launch. This example '
'runs in a Workspace. See Workspaces for background information. 4. '
'Follow the notebook or view it in the docs. 5. Terminate the '
"Workspace when you're done. Ask AI "
'https://docs.anyscale.com/platform/jobs/ 1/2 2/12/25, 9:48 AM Jobs '
'| Anyscale Docs https://docs.anyscale.com/platform/jobs/'}]
为什么它不具可扩展性#
当前常规 RAG 文档摄取方法按顺序处理文档,不利用并行处理。这种缺乏并行处理会在处理大量数据时产生瓶颈。没有分布式处理,扩展到数千份文档 — 每份文档可能包含数十甚至数百页 — 可能会迅速超出单台机器的资源。
此外,在一次操作中嵌入所有文本块可能会导致严重的内存限制并导致性能下降,从而进一步加剧了问题。
在下一个 Notebook 中,我们将演示如何利用 RayData 来构建一个可扩展的文档摄取管道。通过利用 Ray 的分布式计算能力,我们可以显著提高处理效率,减少瓶颈,并为大规模文档摄取实现无缝扩展。