使用离线批推理进行模型验证#
本教程执行一个批推理工作负载,该工作负载连接了以下异构工作负载:
从云存储进行分布式读取
分布式预处理
并行批推理
分布式汇总指标聚合
请注意,本教程从 分布式训练 XGBoost 模型 教程中获取预训练的模型伪影。
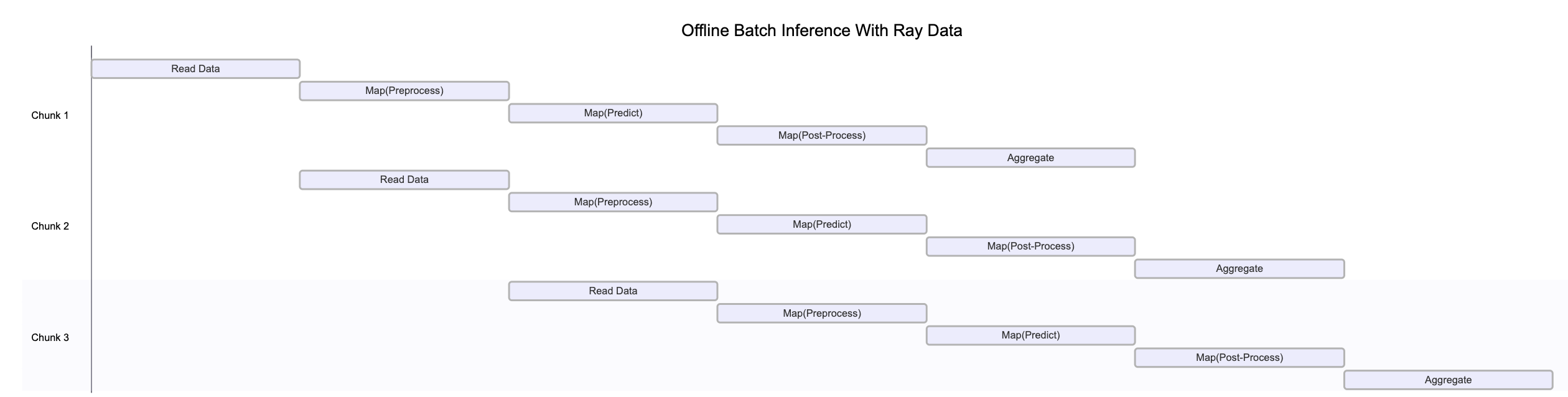
上图说明了 Ray Data 如何在管道的各个阶段同时处理不同数据块。这种并行执行最大化了资源利用率和吞吐量。
请注意,此图为简化示意图,原因如下:
背压机制可能会限制上游算子,以防止下游阶段过载。
数据在管道中移动时,动态重分区经常发生,改变块的数量和大小。
随着集群自动伸缩,可用资源会发生变化。
系统故障可能会中断图中显示的清晰顺序流程。
❌ **传统批处理执行**,非流式处理,如不带流水线的 Spark 和 SageMaker Batch Transform
将整个数据集读入内存或持久化中间格式。
然后才开始应用转换,如 .map、.filter 等。
内存压力更高,启动延迟更高。
✅ Ray Data 的**流式执行**
加载数据块(“blocks”)后立即开始处理,无需等待整个数据集加载完成。
降低内存占用,避免出现内存不足错误,并加快首次输出速度。
通过减少空闲时间来提高资源利用率。
实现低延迟的在线推理管道。
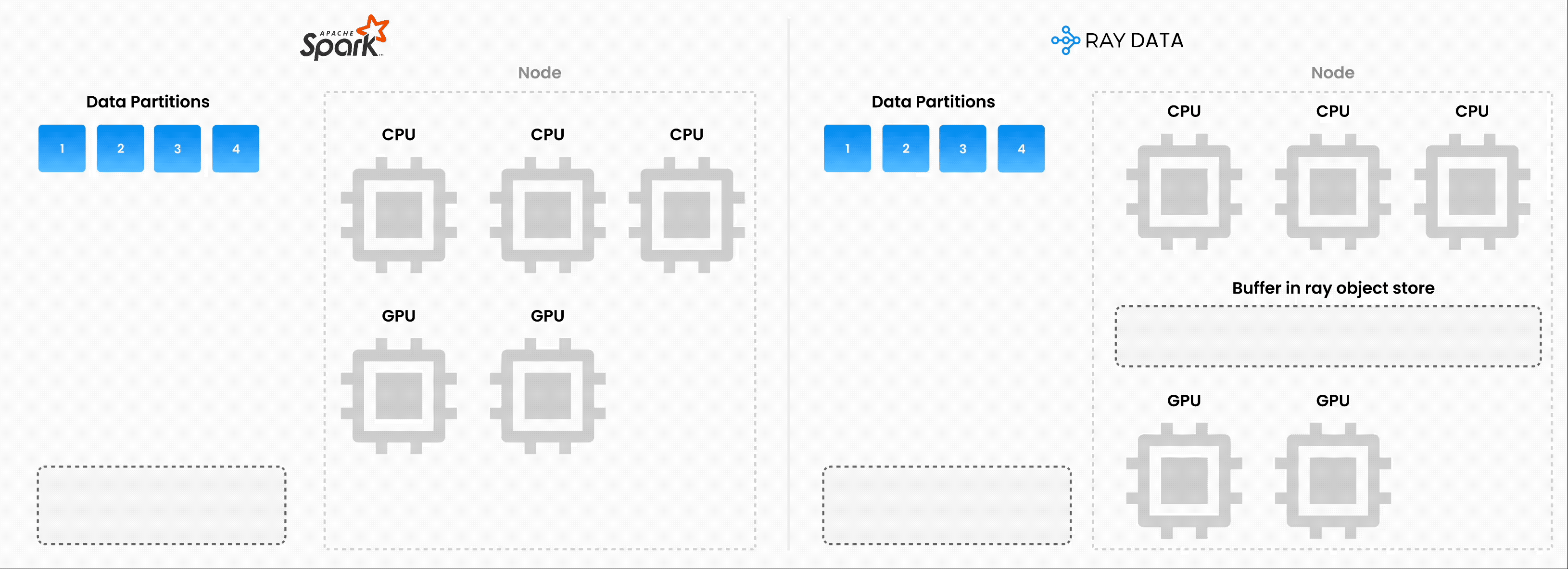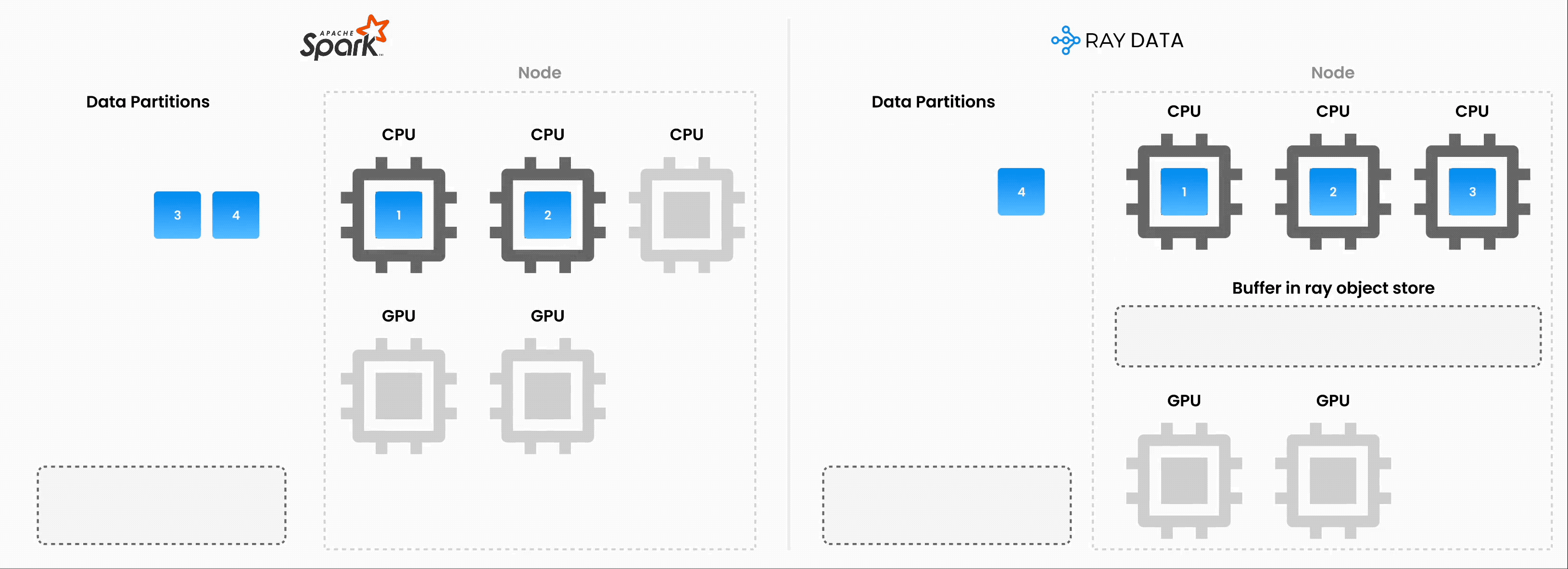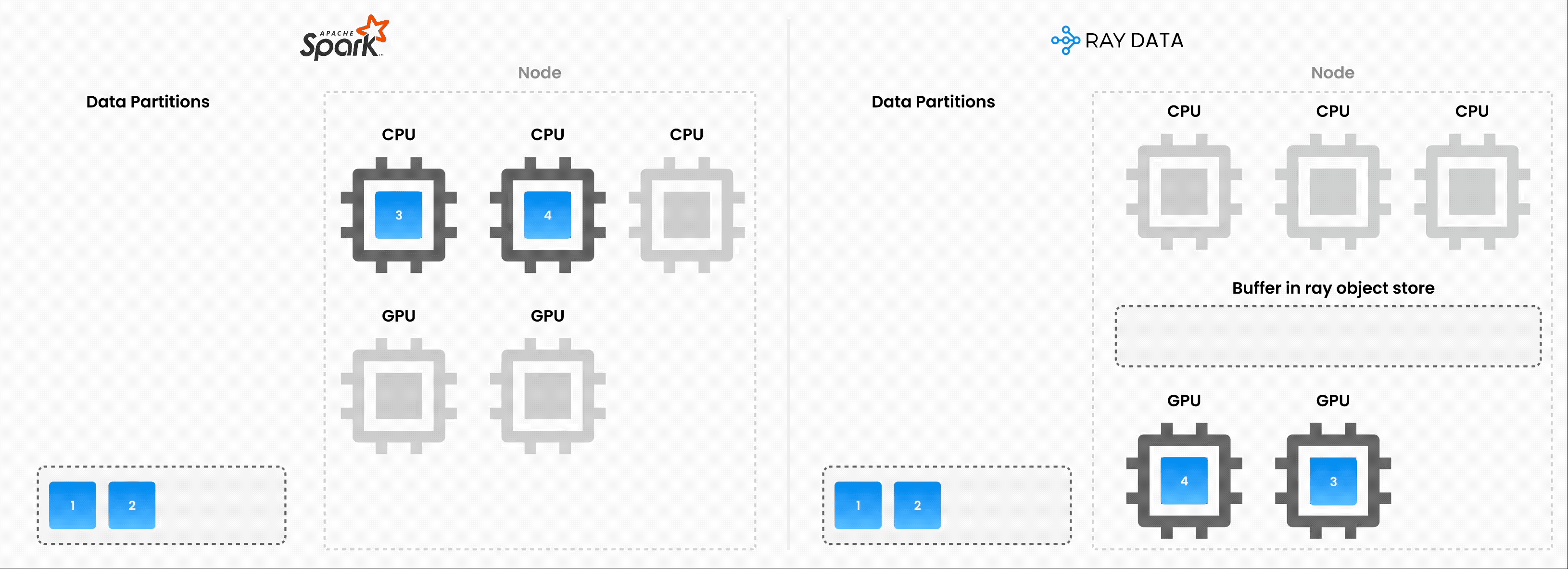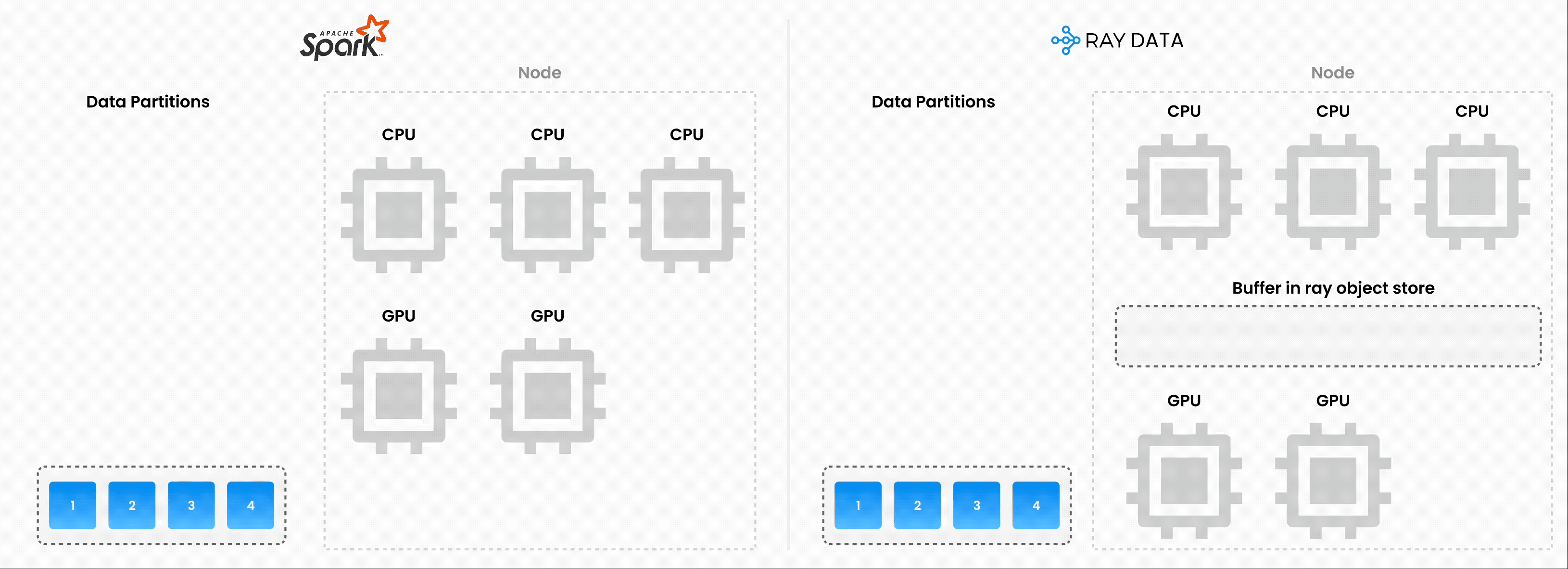
注意:Ray Data 并不是一个实时流处理引擎,如 Flink 或 Kafka Streams。相反,它是一种具有流式执行能力的批处理引擎,这对于迭代式机器学习工作负载、ETL 管道以及训练或推理前的预处理特别有用。与 Spark 和 SageMaker Batch Transform 等解决方案相比,Ray 通常能实现 **2-17 倍的吞吐量提升**。
%load_ext autoreload
%autoreload all
# Enable importing from dist_xgboost package.
import os
import sys
sys.path.append(os.path.abspath(".."))
# Enable Ray Train v2.
os.environ["RAY_TRAIN_V2_ENABLED"] = "1"
# Now it's safe to import from ray.train.
import ray
import dist_xgboost
# Initialize Ray with the dist_xgboost package.
ray.init(runtime_env={"py_modules": [dist_xgboost]})
# Configure Ray Data logging.
ray.data.DataContext.get_current().enable_progress_bars = False
ray.data.DataContext.get_current().print_on_execution_start = False
使用 Ray Data 验证模型#
上一教程《使用 XGBoost 进行分布式训练》训练了一个 XGBoost 模型并将其存储在 MLflow 的伪影存储中。在此步骤中,使用该模型对保留的测试集进行预测。
数据摄取#
使用与之前相同的过程加载测试数据集。
from ray.data import Dataset
def prepare_data() -> tuple[Dataset, Dataset, Dataset]:
"""Load and split the dataset into train, validation, and test sets."""
dataset = ray.data.read_csv("s3://anonymous@air-example-data/breast_cancer.csv")
seed = 42
train_dataset, rest = dataset.train_test_split(test_size=0.3, shuffle=True, seed=seed)
# 15% for validation, 15% for testing.
valid_dataset, test_dataset = rest.train_test_split(test_size=0.5, shuffle=True, seed=seed)
return train_dataset, valid_dataset, test_dataset
_, _, test_dataset = prepare_data()
# Use `take()` to trigger execution because Ray Data uses lazy evaluation mode.
test_dataset.take(1)
2025-04-16 21:14:42,328 INFO worker.py:1660 -- Connecting to existing Ray cluster at address: 10.0.23.200:6379...
2025-04-16 21:14:42,338 INFO worker.py:1843 -- Connected to Ray cluster. View the dashboard at https://session-1kebpylz8tcjd34p4sv2h1f9tg.i.anyscaleuserdata.com
2025-04-16 21:14:42,343 INFO packaging.py:575 -- Creating a file package for local module '/home/ray/default/e2e-xgboost/dist_xgboost'.
2025-04-16 21:14:42,346 INFO packaging.py:367 -- Pushing file package 'gcs://_ray_pkg_fbb1935a37eb6438.zip' (0.02MiB) to Ray cluster...
2025-04-16 21:14:42,347 INFO packaging.py:380 -- Successfully pushed file package 'gcs://_ray_pkg_fbb1935a37eb6438.zip'.
2025-04-16 21:14:42,347 INFO packaging.py:367 -- Pushing file package 'gcs://_ray_pkg_534f9f38a44d4c15f21856eec72c3c338db77a6b.zip' (0.08MiB) to Ray cluster...
2025-04-16 21:14:42,348 INFO packaging.py:380 -- Successfully pushed file package 'gcs://_ray_pkg_534f9f38a44d4c15f21856eec72c3c338db77a6b.zip'.
2025-04-16 21:14:44,609 INFO dataset.py:2809 -- Tip: Use `take_batch()` instead of `take() / show()` to return records in pandas or numpy batch format.
[{'mean radius': 15.7,
'mean texture': 20.31,
'mean perimeter': 101.2,
'mean area': 766.6,
'mean smoothness': 0.09597,
'mean compactness': 0.08799,
'mean concavity': 0.06593,
'mean concave points': 0.05189,
'mean symmetry': 0.1618,
'mean fractal dimension': 0.05549,
'radius error': 0.3699,
'texture error': 1.15,
'perimeter error': 2.406,
'area error': 40.98,
'smoothness error': 0.004626,
'compactness error': 0.02263,
'concavity error': 0.01954,
'concave points error': 0.009767,
'symmetry error': 0.01547,
'fractal dimension error': 0.00243,
'worst radius': 20.11,
'worst texture': 32.82,
'worst perimeter': 129.3,
'worst area': 1269.0,
'worst smoothness': 0.1414,
'worst compactness': 0.3547,
'worst concavity': 0.2902,
'worst concave points': 0.1541,
'worst symmetry': 0.3437,
'worst fractal dimension': 0.08631,
'target': 0}]
开发期间使用
materialize():materialize()方法会在 Ray 的共享内存对象存储中执行并存储数据集。这种行为会创建一个检查点,以便将来的操作可以从此点开始,而无需从头开始重新运行所有操作。选择合适的混洗策略:Ray Data 提供了各种 混洗策略,包括局部混洗和每个 epoch 的混洗。您需要混洗此数据集,因为原始数据按类别对项目进行分组。
接下来,以与训练期间相同的方式转换输入数据。从伪影注册表中获取预处理器。
import pickle
from dist_xgboost.constants import preprocessor_fname
from dist_xgboost.data import get_best_model_from_registry
best_run, best_artifacts_dir = get_best_model_from_registry()
with open(os.path.join(best_artifacts_dir, preprocessor_fname), "rb") as f:
preprocessor = pickle.load(f)
现在,在 Ray Data 管道中定义转换步骤。不要使用 .map() 单独处理每个项目,而是使用 Ray Data 的 map_batches 方法一次处理整个批次,这样效率更高。
def transform_with_preprocessor(batch_df, preprocessor):
# The preprocessor doesn't include the `target` column,
# so remove it temporarily, then add it back.
target = batch_df.pop("target")
transformed_features = preprocessor.transform_batch(batch_df)
transformed_features["target"] = target
return transformed_features
# Apply the transformation to each batch.
test_dataset = test_dataset.map_batches(
transform_with_preprocessor,
fn_kwargs={"preprocessor": preprocessor},
batch_format="pandas",
batch_size=1000,
)
test_dataset.show(1)
{'mean radius': 0.4202879281965173, 'mean texture': 0.2278148207774012, 'mean perimeter': 0.35489846800755104, 'mean area': 0.29117590184541364, 'mean smoothness': -0.039721410464208406, 'mean compactness': -0.30321758777095337, 'mean concavity': -0.2973304995033593, 'mean concave points': 0.05629912285695481, 'mean symmetry': -0.6923528276633714, 'mean fractal dimension': -1.0159489469979848, 'radius error': -0.1244372811541358, 'texture error': -0.1073358496664629, 'perimeter error': -0.2253381140213174, 'area error': 0.001804996358367429, 'smoothness error': -0.8087740189276656, 'compactness error': -0.1437977993323648, 'concavity error': -0.3926326901399853, 'concave points error': -0.34157926393517024, 'symmetry error': -0.5862955941365042, 'fractal dimension error': -0.496152478599194, 'worst radius': 0.7695260874215265, 'worst texture': 1.1287525414418031, 'worst perimeter': 0.6310282171135395, 'worst area': 0.6506421499178707, 'worst smoothness': 0.39052158034274154, 'worst compactness': 0.6735246675401986, 'worst concavity': 0.06668871795848759, 'worst concave points': 0.5859784499947507, 'worst symmetry': 0.8525444557664399, 'worst fractal dimension': 0.14066370266791928, 'target': 0}
加载已训练模型#
现在您已经定义了预处理管道,可以运行批推理了。从伪影注册表中加载模型。
from ray.train import Checkpoint
from ray.train.xgboost import RayTrainReportCallback
checkpoint = Checkpoint.from_directory(best_artifacts_dir)
model = RayTrainReportCallback.get_model(checkpoint)
运行批推理#
接下来,运行推理步骤。为了避免为每个批次重复加载模型,请定义一个可重用类,该类可以使用相同的 XGBoost 模型处理不同的批次。
import pandas as pd
import xgboost
from dist_xgboost.data import load_model_and_preprocessor
class Validator:
def __init__(self):
_, self.model = load_model_and_preprocessor()
def __call__(self, batch: pd.DataFrame) -> pd.DataFrame:
# Remove the target column for inference.
target = batch.pop("target")
dmatrix = xgboost.DMatrix(batch)
predictions = self.model.predict(dmatrix)
results = pd.DataFrame({"prediction": predictions, "target": target})
return results
现在,通过分批处理数据来并行化模型的推理。
test_predictions = test_dataset.map_batches(
Validator,
concurrency=4, # Number of model replicas.
batch_format="pandas",
)
test_predictions.show(1)
2025-04-16 21:14:56,496 WARNING actor_pool_map_operator.py:287 -- To ensure full parallelization across an actor pool of size 4, the Dataset should consist of at least 4 distinct blocks. Consider increasing the parallelism when creating the Dataset.
{'prediction': 0.031001044437289238, 'target': 0}
计算评估指标#
现在您有了预测结果,可以评估模型的准确率、精确率、召回率和 F1 分数。计算测试子集上的真阳性、真阴性、假阳性和假阴性数量。
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
def confusion_matrix_batch(batch, threshold=0.5):
# Apply a threshold to get binary predictions.
batch["prediction"] = (batch["prediction"] > threshold).astype(int)
result = {}
cm = confusion_matrix(batch["target"], batch["prediction"], labels=[0, 1])
result["TN"] = cm[0, 0]
result["FP"] = cm[0, 1]
result["FN"] = cm[1, 0]
result["TP"] = cm[1, 1]
return pd.DataFrame(result, index=[0])
test_results = test_predictions.map_batches(confusion_matrix_batch, batch_format="pandas", batch_size=1000)
最后,将所有批次的混淆矩阵结果聚合起来,得到全局计数。此步骤将具体化数据集并执行所有先前声明的惰性转换。
# Sum all confusion matrix values across batches.
cm_sums = test_results.sum(["TN", "FP", "FN", "TP"])
# Extract confusion matrix components.
tn = cm_sums["sum(TN)"]
fp = cm_sums["sum(FP)"]
fn = cm_sums["sum(FN)"]
tp = cm_sums["sum(TP)"]
# Calculate metrics.
accuracy = (tp + tn) / (tp + tn + fp + fn)
precision = tp / (tp + fp) if (tp + fp) > 0 else 0
recall = tp / (tp + fn) if (tp + fn) > 0 else 0
f1 = 2 * precision * recall / (precision + recall) if (precision + recall) > 0 else 0
metrics = {"precision": precision, "recall": recall, "f1": f1, "accuracy": accuracy}
2025-04-16 21:15:01,144 WARNING actor_pool_map_operator.py:287 -- To ensure full parallelization across an actor pool of size 4, the Dataset should consist of at least 4 distinct blocks. Consider increasing the parallelism when creating the Dataset.
print("Validation results:")
for key, value in metrics.items():
print(f"{key}: {value:.4f}")
Validation results:
precision: 0.9464
recall: 0.9815
f1: 0.9636
accuracy: 0.9535
以下是预期输出:
Validation results:
precision: 0.9574
recall: 1.0000
f1: 0.9783
accuracy: 0.9767
可观察性#
Ray Data 提供了内置的可观测性功能,可帮助您监控和调试数据处理管道。
生产部署#
您可以将培训工作负载包装成生产级的 Anyscale 作业。请参阅 API 参考。
# Production batch job.
anyscale job submit --name=validate-xboost-breast-cancer-model \
--containerfile="${WORKING_DIR}/containerfile" \
--working-dir="${WORKING_DIR}" \
--exclude="" \
--max-retries=0 \
-- python dist_xgboost/infer.py
请注意,为了使此命令成功,请先配置 MLflow,使其将伪影存储在跨集群可读的存储中。Anyscale 提供各种开箱即用的存储选项,例如 默认存储桶,以及集群、用户和云级别共享的 自动挂载的网络存储。您也可以设置自己的网络挂载或存储桶。
总结#
在本教程中,您:
使用从云存储进行的分布式读取加载了测试数据集。
以流式方式转换了数据集,使用了与训练期间相同的预处理器。
进行了一个验证管道,以:
使用多个模型副本对测试数据进行预测。
为每个批次计算混淆矩阵的组成部分。
跨所有批次聚合结果。
计算了关键性能指标,如精确率、召回率、F1 分数和准确率。
使用 Ray Data 的分布式处理能力,相同的代码可以高效地在 TB 级数据集上运行,而无需修改。
下一教程将展示如何使用 Ray Serve 为在线推理服务此 XGBoost 模型。

