构建基础 RAG 应用#
本教程使用 Ray 生态系统组件演示了一个完整的检索增强生成 (RAG) 系统,用于可扩展的 AI 工作流。
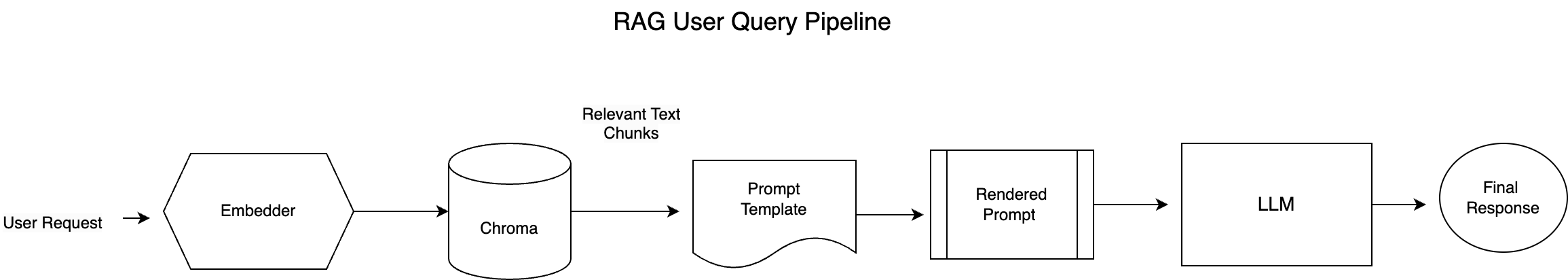
由于我们已经在笔记本 #2 中构建了数据摄取管道,因此我们将只展示如何为 RAG 构建用户查询管道。
它在一个可执行的管道中展示了嵌入生成、向量搜索、上下文感知提示和流式响应传递。
架构图如下
注意:本教程针对 Anyscale 平台进行了优化。在开源 Ray 上运行时,需要额外的配置。例如,您需要手动
- 配置您的 Ray 集群:设置您的多节点环境(包括主节点和工作节点),并管理资源分配(例如,自动伸缩、GPU/CPU 分配),而无需 Anyscale 的自动化。有关详细信息,请参阅 Ray 集群设置文档:https://docs.rayai.org.cn/en/latest/cluster/getting-started.html。
- 管理依赖项:在每个节点上安装和管理依赖项,因为您将无法使用 Anyscale 基于 Docker 的依赖项管理。请参阅 Ray 安装指南,了解在环境中安装和更新 Ray 的说明:https://docs.rayai.org.cn/en/latest/ray-core/handling-dependencies.html。
- 设置存储:配置您自己的分布式或共享存储系统(而不是依赖 Anyscale 的集成集群存储)。请查看 Ray 集群配置指南,了解有关设置共享存储解决方案的建议:https://docs.rayai.org.cn/en/latest/train/user-guides/persistent-storage.html。
先决条件#
在进行下一步之前,请确保您已具备所有必需的先决条件。
验证 LLM 服务#
首先,让我们验证 LLM 服务是否可用。
from rag_utils import LLMClient
# Initialize client
model_id='Qwen/Qwen2.5-32B-Instruct' ## model id need to be same as your deployment
base_url = "https://llm-service-qwen-32b-jgz99.cld-kvedzwag2qa8i5bj.s.anyscaleuserdata.com/" ## replace with your own service base url
api_key = "a1ndpMKaXi76sTIfr_afmx8HynFA1fg-TGaZ2gUuDG0" ## replace with your own api key
client = LLMClient(base_url=base_url, api_key=api_key, model_id=model_id)
prompt = "what is anyscale jobs"
print("Model response:")
for token in client.get_response_streaming(prompt, temperature=0):
print(token, end="")
print() # For newline after the streamed response
Model response:
Anyscale Jobs likely refers to job opportunities or roles within the context of Anyscale, a company that specializes in scalable computing solutions. Anyscale is known for developing Ray, an open-source framework for building distributed applications. The company focuses on making it easier for developers and researchers to scale their applications and machine learning models across multiple machines.
If you're looking for information on specific job openings at Anyscale, you would typically find these on the company's official website under a "Careers" or "Jobs" section, or on popular job listing platforms. Positions might include roles in software engineering, machine learning, data science, and other technical fields, given the company's focus on scalable computing and distributed systems.
观察与为何我们需要 RAG?#
该响应引用了 Anyscale 的职位空缺,而不是解释“Anyscale jobs”在平台中的含义:https://docs.anyscale.com/platform/jobs/
这表明了 RAG 的必要性——通过整合特定领域的上下文,我们帮助 LLM 产生更准确的答案。
构建嵌入器#
与之前的教程类似,我们使用 SentenceTransformer 库将文本字符串转换为数字嵌入。嵌入器会自动利用支持 CUDA 的 GPU(如果可用),使其在单次和批量处理方面都高效。
from typing import Dict, List, Union
import torch
import numpy as np
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer
class Embedder:
def __init__(self, model_name: str = "intfloat/multilingual-e5-large-instruct"):
self.model_name = model_name
self.model = SentenceTransformer(
self.model_name,
device="cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
)
def embed_single(self, text: str) -> np.ndarray:
"""Generate an embedding for a single text string."""
return self.model.encode(text, convert_to_numpy=True)
def embed_batch(self, texts: List[str]) -> np.ndarray:
"""Generate embeddings for a batch (list) of text strings."""
return self.model.encode(texts, convert_to_numpy=True)
查询 Chroma DB#
与之前教程中的 ChromaWrite 类类似,我们定义了一个 ChromaQuerier 类,它充当 Chroma 向量存储的接口,能够根据与提供的查询嵌入的相似性高效检索文档块。
它通过根据定义的得分阈值重新格式化和过滤原始结果来处理它们,确保只返回最相关的信息。作为检索增强生成 (RAG) 工作流的一部分,此设置有助于将精确、上下文相关的数据整合到后续的生成步骤中。
score_threshold 参数设置了要被视为相关的结果的最低可接受相似度得分。在此代码中,每个结果的得分计算为 1 减去其距离,这意味着较低的距离(表示较高的相似度)会产生较高的得分。通过过滤掉得分低于 score_threshold(默认为 0.8)的任何结果,代码确保只返回最具上下文相关性的文档。
我们还实现了两个特殊方法,__getstate__ 和 __setstate__,它们是 Python 序列化协议中的特殊钩子。
__getstate__:通过删除无法序列化的属性来准备对象以进行序列化,确保只保存必要的状态。__setstate__:在反序列化后通过恢复其状态并重新初始化无法序列化的组件来重建对象,以便对象保持完全功能。
这两个函数将阻止在使用 Ray Data 进行批量处理时,使用 `map_batches` 时出现类似 TypeError: cannot pickle 'weakref.ReferenceType' object 的错误。
from pprint import pprint
import chromadb
class ChromaQuerier:
"""
A class to query a Chroma database collection and return formatted search results.
"""
def __init__(
self,
chroma_path: str,
chroma_collection_name: str,
score_threshold: float = 0.8 # Define a default threshold value if needed.
):
"""
Initialize the ChromaQuerier with the specified Chroma DB settings and score threshold.
"""
self.chroma_path = chroma_path
self.chroma_collection_name = chroma_collection_name
self.score_threshold = score_threshold
# Initialize the persistent client and collection.
self._init_chroma_client()
def _init_chroma_client(self):
"""
Initialize or reinitialize the Chroma client and collection.
"""
self.chroma_client = chromadb.PersistentClient(path=self.chroma_path)
self.collection = self.chroma_client.get_or_create_collection(name=self.chroma_collection_name)
def __getstate__(self):
"""
Customize pickling by excluding the unpickleable Chroma client and collection.
"""
state = self.__dict__.copy()
state.pop("chroma_client", None)
state.pop("collection", None)
return state
def __setstate__(self, state):
"""
Restore the state and reinitialize the Chroma client and collection.
"""
self.__dict__.update(state)
self._init_chroma_client()
def _reformat(self, chroma_results: dict) -> list:
"""
Reformat Chroma DB results into a flat list of dictionaries.
"""
reformatted = []
metadatas = chroma_results.get("metadatas", [])
documents = chroma_results.get("documents", [])
distances = chroma_results.get("distances", [])
chunk_index = 1
for meta_group, doc_group, distance_group in zip(metadatas, documents, distances):
for meta, text, distance in zip(meta_group, doc_group, distance_group):
entry = {
"chunk_index": chunk_index,
"chunk_id": meta.get("chunk_id"),
"doc_id": meta.get("doc_id"),
"page_number": meta.get("page_number"),
"source": meta.get("source"),
"text": text,
"distance": distance,
"score": 1 - distance
}
reformatted.append(entry)
chunk_index += 1
return reformatted
def _reformat_batch(self, chroma_results: dict) -> list:
"""
Reformat batch Chroma DB results into a list where each element corresponds
to a list of dictionaries for each query embedding.
"""
batch_results = []
metadatas = chroma_results.get("metadatas", [])
documents = chroma_results.get("documents", [])
distances = chroma_results.get("distances", [])
for meta_group, doc_group, distance_group in zip(metadatas, documents, distances):
formatted_results = []
chunk_index = 1 # Reset index for each query result.
for meta, text, distance in zip(meta_group, doc_group, distance_group):
entry = {
"chunk_index": chunk_index,
"chunk_id": meta.get("chunk_id"),
"doc_id": meta.get("doc_id"),
"page_number": meta.get("page_number"),
"source": meta.get("source"),
"text": text,
"distance": distance,
"score": 1 - distance
}
formatted_results.append(entry)
chunk_index += 1
batch_results.append(formatted_results)
return batch_results
def _filter_by_score(self, results: list) -> list:
"""
Filter out results with a score lower than the specified threshold.
"""
return [result for result in results if result["score"] >= self.score_threshold]
def query(self, query_embedding, n_results: int = 3) -> list:
"""
Query the Chroma collection for the top similar documents based on the provided embedding.
The results are filtered based on the score threshold.
Parameters:
query_embedding (list or np.ndarray): The input embedding vector.
n_results (int): Number of top similar results to return.
Returns:
list: A list of formatted and filtered search result dictionaries.
"""
# Convert numpy array to list if necessary.
if isinstance(query_embedding, np.ndarray):
query_embedding = query_embedding.tolist()
results = self.collection.query(
query_embeddings=query_embedding,
n_results=n_results,
include=["documents", "metadatas", "distances"]
)
formatted_results = self._reformat(results)
filtered_results = self._filter_by_score(formatted_results)
return filtered_results
def query_batch(self, query_embeddings, n_results: int = 3) -> list:
"""
Query the Chroma collection for the top similar documents for a batch of embeddings.
Each query embedding in the input list returns its own set of results, filtered based on the score threshold.
Parameters:
query_embeddings (list): A list of embeddings (each as a list or np.ndarray).
n_results (int): Number of top similar results to return for each query embedding.
Returns:
list: A list where each element is a list of formatted and filtered search result dictionaries
for the corresponding query embedding.
"""
# Process each embedding: if any is a numpy array, convert it to list.
processed_embeddings = [
emb.tolist() if isinstance(emb, np.ndarray) else emb
for emb in query_embeddings
]
# Query the collection with the batch of embeddings.
results = self.collection.query(
query_embeddings=processed_embeddings,
n_results=n_results,
include=["documents", "metadatas", "distances"]
)
# Reformat the results into batches.
batch_results = self._reformat_batch(results)
# Filter each query's results based on the score threshold.
filtered_batch = [self._filter_by_score(results) for results in batch_results]
return filtered_batch
渲染基础 RAG 提示#
创建一个包含检索到的上下文和用户问题的提示。此提示指导 LLM 生成一个基于上下文的答案。
我们使用的是 Langchain 的 rag bot 的一个基础提示:https://python.langchain.ac.cn/docs/tutorials/rag/
注意:提示的质量并非最优;在下一篇关于提示工程的教程中,我们将展示如何改进它。
def render_basic_rag_prompt(user_request, context):
prompt = f"""Use the following pieces of context to answer the question at the end.
If you don't know the answer, just say that you don't know, don't try to make up an answer.
Use three sentences maximum and keep the answer as concise as possible.
Always say "thanks for asking!" at the end of the answer.
{context}
Question: {user_request}
Helpful Answer:"""
return prompt.strip()
连接 RAG 的组件#
将嵌入器、Chroma 查询器和 LLM 服务集成到一个完整的 RAG 管道中。
EMBEDDER_MODEL_NAME = "intfloat/multilingual-e5-large-instruct"
CHROMA_PATH = "/mnt/cluster_storage/vector_store"
CHROMA_COLLECTION_NAME = "anyscale_jobs_docs_embeddings"
# Initialize the querier.
querier = ChromaQuerier(CHROMA_PATH, CHROMA_COLLECTION_NAME, score_threshold=0.8)
embedder = Embedder(EMBEDDER_MODEL_NAME)
# Perform the user request.
user_request = "what is a anyscale job"
embedding = embedder.embed_single(user_request)
formatted_results = querier.query(embedding, n_results=10)
# Print the formatted query results.
print("Query Results:")
pprint(formatted_results)
# Render the prompt.
prompt = render_basic_rag_prompt(user_request, context=formatted_results)
print("Rendered Prompt:")
pprint(prompt)
Query Results:
[{'chunk_id': '55b8db89-0aa6-460c-ae3a-284241f5865c',
'chunk_index': 1,
'distance': 0.10053980350494385,
'doc_id': '7b170e3d-4081-4527-a737-1da022a364c4',
'page_number': 1,
'score': 0.8994601964950562,
'source': 'anyscale-rag-application/100-docs/Jobs.txt',
'text': '2/12/25, 9:48 AM Jobs | Anyscale Docs Jobs Run discrete workloads '
'in production such as batch inference, bulk embeddings generation, '
'or model fine-tuning. Anyscale Jobs allow you to submit '
'applications developed on workspaces to a standalone Ray cluster '
'for execution. Built for production and designed to fit into your '
'CI/CD pipeline, jobs ensure scalable and reliable performance. How '
'does it work? # When you’re ready to promote an app to production, '
'submit a job from the workspace using anyscale job submit . '
'Anyscale Jobs have the following features: Scalability: Rapid '
'scaling to thousands of cloud instances, adjusting computing '
'resources to match application demand. Fault tolerance: Retries for '
'failures and automatic rescheduling to an alternative cluster for '
'unexpected failures like running out of memory. Monitoring and '
'observability: Persistent dashboards that allow you to observe '
'tasks in real time and email alerts upon successf ul job '
'completion. Get started 1. Sign in or sign up for an account. 2. '
'Select the Intro to Jobs example. 3. Select Launch. This example '
'runs in a Workspace. See Workspaces for background information. 4. '
'Follow the notebook or view it in the docs. 5. Terminate the '
"Workspace when you're done. Ask AI "
'https://docs.anyscale.com/platform/jobs/ 1/2 2/12/25, 9:48 AM Jobs '
'| Anyscale Docs https://docs.anyscale.com/platform/jobs/ 2/2'},
{'chunk_id': 'fdd75966-04d9-43d2-8e3e-b85e8387d086',
'chunk_index': 2,
'distance': 0.11302393674850464,
'doc_id': '82efb8cd-2181-47cb-9389-ff101cc68674',
'page_number': 2,
'score': 0.8869760632514954,
'source': 'anyscale-rag-application/100-docs/Create_and_manage_jobs.pdf',
'text': '2/12/25, 9:48 AM Create and manage jobs | Anyscale Docs Defining a '
'job With the CLI, you can define jobs in a YAML file and submit '
'them by referencing the YAML: anyscale job submit --config-file '
'config.yaml For an example of defining a job in a YAML, see the '
'reference docs. Waiting on a job You can block CLI and SDK commands '
'until a job enters a specified state. By default, '
'JobState.SUCCEEDED is used. See all available states in the '
'reference docs. CLI Python SDK anyscale job wait -n job-wait When '
'you submit a job, you can specify --wait , which waits for the job '
'to succeed or exits if the job fails. anyscale job submit -n '
'job-wait --wait -- sleep 30 For more information on submitting jobs '
'with the CLI, see the reference docs. Terminating a job You can '
'terminate a job from the Job page or using the CLI/SDK: CLI Python '
'SDK https://docs.anyscale.com/platform/jobs/manage-jobs 2/5'},
{'chunk_id': '23bf61db-155a-4a1a-a74f-669409c92303',
'chunk_index': 3,
'distance': 0.11444741487503052,
'doc_id': '91ddd49b-9e23-4e58-9143-bbac61ee2157',
'page_number': 1,
'score': 0.8855525851249695,
'source': 'anyscale-rag-application/100-docs/Job_schedules.html',
'text': 'anyscale.job.terminate(name="my-job") For more information on '
'terminating jobs with the SDK, see the reference docs. Archiving a '
'job\u200b Archiving jobs hide them from the job list page, but you '
'can still access them through the CLI and SDK. The cluster '
'associated with an archived job is archived automatically. To be '
'archived, jobs must be in a terminal state. You must have created '
'the job or be an organization admin to archive the job. You can '
'archive jobs in Anyscale console or through the CLI/SDK: CLI Python '
"SDK anyscale job archive --id 'prodjob_...' For more information on "
'archiving jobs with the CLI, see the reference docs. import '
'anyscale\n'
'\n'
'anyscale.job.archive(name="my-job") For more information on '
'archiving jobs with the SDK, see the reference docs. Managing '
'dependencies\u200b When developing Anyscale jobs, you may need to '
'include additional Python packages or system-level dependencies. '
'There are several ways to manage these dependencies: Using a '
'requirements.txt file\u200b The simplest way to manage Python '
'package dependencies is by using a requirements.txt file. Create a '
'requirements.txt file in your project directory: emoji==2.12.1\n'
'numpy==1.21.0 When submitting your job, include the -r or '
'--requirements flag: CLI Python SDK anyscale job submit '
'--config-file job.yaml -r ./requirements.txt import anyscale\n'
'from anyscale.job.models import JobConfig\n'
'\n'
'config = JobConfig(\n'
' name="my-job",\n'
' entrypoint="python main.py",\n'
' working_dir=".",\n'
' requirements="./requirements.txt"\n'
')\n'
'\n'
'anyscale.job.submit(config) This method works well for '
'straightforward Python package dependencies. Anyscale installs '
"these packages in the job's environment before running your code. "
'Using a custom container\u200b For more complex dependency '
'management, including system-level packages or specific environment '
'configurations, use a custom container: Create a Dockerfile: FROM '
'anyscale/ray:2.10.0-py310\n'
'\n'
'# Install system dependencies if needed\n'
'RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y <your-system-packages>'},
{'chunk_id': '13683649-bcdc-444d-866f-36cafcb132c9',
'chunk_index': 4,
'distance': 0.11574643850326538,
'doc_id': '91ddd49b-9e23-4e58-9143-bbac61ee2157',
'page_number': 1,
'score': 0.8842535614967346,
'source': 'anyscale-rag-application/100-docs/Job_schedules.html',
'text': 'Create and manage jobs Submitting a job\u200b To submit your job to '
'Anyscale, use the Python SDK or CLI and pass in any additional '
'options or configurations for the job. By default, Anyscale uses '
'your workspace or cloud to provision a cluster to run your job. You '
'can define a custom cluster through a compute config or specify an '
'existing cluster. Once submitted, Anyscale runs the job as '
'specified in the entrypoint command, which is typically a Ray Job. '
"If the run doesn't succeed, the job restarts using the same "
'entrypoint up to the number of max_retries. CLI Python SDK anyscale '
'job submit --name=my-job \\\n'
' --working-dir=. --max-retries=5 \\\n'
' --image-uri="anyscale/image/IMAGE_NAME:VERSION" \\\n'
' --compute-config=COMPUTE_CONFIG_NAME \\\n'
' -- python main.py With the CLI, you can either specify an '
'existing compute config with --compute-config=COMPUTE_CONFIG_NAME '
'or define a new one in a job YAML. For more information on '
'submitting jobs with the CLI, see the reference docs. import '
'anyscale\n'
'from anyscale.job.models import JobConfig\n'
'\n'
'config = JobConfig(\n'
' name="my-job",\n'
' entrypoint="python main.py",\n'
' working_dir=".",\n'
' max_retries=5,\n'
' image_uri="anyscale/image/IMAGE_NAME:VERSION",\n'
' compute_config="COMPUTE_CONFIG_NAME"\n'
')'},
{'chunk_id': '3167ba0b-2aff-4f69-8dbe-7a8cdc725005',
'chunk_index': 5,
'distance': 0.11749774217605591,
'doc_id': '7a7730fa-96a1-4775-896a-11deac94d668',
'page_number': 1,
'score': 0.8825022578239441,
'source': 'anyscale-rag-application/100-docs/Job_queues.pptx',
'text': '2/12/25, 9:48 AM\tJob queues | Anyscale Docs Job queues A job queue '
'enables sophisticated scheduling and execution algorithms for '
'Anyscale Jobs. This feature improves resource utilization and '
'reduces provisioning times by enabling multiple jobs to share a '
'single cluster. Anyscale supports flexible scheduling algorithms, '
'including FIFO (first-in, first-out), LIFO (last-in, first-out), '
'and priority-based scheduling. Job processing Anyscale job queues '
'optimize resource utilization and throughput by using sophisticated '
'scheduling to run multiple jobs on the same cluster. Submission: '
'The typical Anyscale Job submission workflow adds the job to the '
'specified queue. Scheduling: Based on the scheduling policy, '
'Anyscale determines ordering of the jobs in the queue and picks '
'jobs at the top of the queue for scheduling. Anyscale schedules no '
'more than the specified max-concurrency jobs for running on a '
'cluster at the same time. Execution: Jobs run until completion, '
'including retries up to the specified number of max_retries . '
'Anyscale provisions a cluster when you submit the first job in a '
'queue, and continues running until there are no more jobs in the '
'queue and it idles. Create a job queue Creating a job queue is '
'similar to creating a standalone Anyscale Job. In your job.yaml '
'file, specify additional job queue configurations: CLI\tPython SDK '
'Ask AI https://docs.anyscale.com/platform/jobs/job-queues 1/5'},
{'chunk_id': '8c158e24-22e2-4984-a402-2331cf0896fc',
'chunk_index': 6,
'distance': 0.12043756246566772,
'doc_id': '82efb8cd-2181-47cb-9389-ff101cc68674',
'page_number': 1,
'score': 0.8795624375343323,
'source': 'anyscale-rag-application/100-docs/Create_and_manage_jobs.pdf',
'text': '2/12/25, 9:48 AM Create and manage jobs | Anyscale Docs Create and '
'manage jobs Submitting a job To submit your job to Anyscale, use '
'the Python SDK or CLI and pass in any additional options or '
'configurations for the job. By default, Anyscale uses your '
'workspace or cloud to provision a cluster to run your job. You can '
'define a custom cluster through a compute config or specify an '
'existing cluster. Once submitted, Anyscale runs the job as '
'specified in the entrypoint command, which is typically a Ray Job. '
"If the run doesn't succeed, the job restarts using the same "
'entrypoint up to the number of max_retries . CLI Python SDK '
'anyscale job submit --name=my-job \\ --working-dir=. '
'--max-retries=5 \\ --image-uri="anyscale/image/IMAGE_NAME:VERSION" '
'\\ --compute-config=COMPUTE_CONFIG_NAME \\ -- python main.py With '
'the CLI, you can either specify an existing compute config with '
'--compute- config=COMPUTE_CONFIG_NAME or define a new one in a job '
'YAML. For more information on submitting jobs with the CLI, see the '
'reference docs. TIP For large-scale, compute-intensive jobs, avoid '
'scheduling Ray tasks onto the head node because it manages '
'cluster-level orchestration. To do that, set the CPU resource on '
'the head node to 0 in your compute config. Ask AI '
'https://docs.anyscale.com/platform/jobs/manage-jobs 1/5'},
{'chunk_id': '2d0623d0-911f-471a-9649-a61c0b2db411',
'chunk_index': 7,
'distance': 0.12314975261688232,
'doc_id': '82efb8cd-2181-47cb-9389-ff101cc68674',
'page_number': 5,
'score': 0.8768502473831177,
'source': 'anyscale-rag-application/100-docs/Create_and_manage_jobs.pdf',
'text': '2/12/25, 9:48 AM Create and manage jobs | Anyscale Docs Using '
'pre-built custom images For frequently used environments, you can '
'build and reuse custom images: 1. Build the image: CLI Python SDK '
'anyscale image build -n my-custom-image --containerfile Dockerfile '
'2. Use the built image in your job submission: CLI Python SDK '
'anyscale job submit --config-file job.yaml --image-uri '
'anyscale/image/my- custom-image:1 This approach is efficient for '
'teams working on multiple jobs that share the same dependencies. '
'https://docs.anyscale.com/platform/jobs/manage-jobs 5/5'},
{'chunk_id': '96285d69-2f27-4fb6-81be-31a4ededffba',
'chunk_index': 8,
'distance': 0.1248595118522644,
'doc_id': '82efb8cd-2181-47cb-9389-ff101cc68674',
'page_number': 3,
'score': 0.8751404881477356,
'source': 'anyscale-rag-application/100-docs/Create_and_manage_jobs.pdf',
'text': '2/12/25, 9:48 AM Create and manage jobs | Anyscale Docs anyscale '
"job terminate --id 'prodjob_...' For more information on "
'terminating jobs with the CLI, see the reference docs. Archiving a '
'job Archiving jobs hide them from the job list page, but you can '
'still access them through the CLI and SDK. The cluster associated '
'with an archived job is archived automatically. To be archived, '
'jobs must be in a terminal state. You must have created the job or '
'be an organization admin to archive the job. You can archive jobs '
'in Anyscale console or through the CLI/SDK: CLI Python SDK anyscale '
"job archive --id 'prodjob_...' For more information on archiving "
'jobs with the CLI, see the reference docs. Managing dependencies '
'When developing Anyscale jobs, you may need to include additional '
'Python packages or system- level dependencies. There are several '
'ways to manage these dependencies: Using a requirements.txt file '
'The simplest way to manage Python package dependencies is by using '
'a requirements.txt file. 1. Create a requirements.txt file in your '
'project directory: emoji==2.12.1 numpy==1.21.0 '
'https://docs.anyscale.com/platform/jobs/manage-jobs 3/5'},
{'chunk_id': 'd7c57ead-0228-4c49-bb77-37b67aed463d',
'chunk_index': 9,
'distance': 0.12725389003753662,
'doc_id': '91ddd49b-9e23-4e58-9143-bbac61ee2157',
'page_number': 1,
'score': 0.8727461099624634,
'source': 'anyscale-rag-application/100-docs/Job_schedules.html',
'text': 'config = JobConfig(\n'
' name="my-job",\n'
' entrypoint="python main.py",\n'
' working_dir=".",\n'
' max_retries=5,\n'
' image_uri="anyscale/image/IMAGE_NAME:VERSION",\n'
' compute_config="COMPUTE_CONFIG_NAME"\n'
')\n'
'\n'
'anyscale.job.submit(config) With the SDK, you can either specify an '
'existing compute config or define a new one using the compute '
'config API. For more information on submitting jobs with the SDK, '
'see the reference docs. For a complete list of supported options '
'defining a JobConfig, see the reference docs for JobConfig. tip For '
'large-scale, compute-intensive jobs, avoid scheduling Ray tasks '
'onto the head node because it manages cluster-level orchestration. '
'To do that, set the CPU resource on the head node to 0 in your '
'compute config. Defining a job\u200b With the CLI, you can define '
'jobs in a YAML file and submit them by referencing the YAML: '
'anyscale job submit --config-file config.yaml For an example of '
'defining a job in a YAML, see the reference docs. Waiting on a '
'job\u200b You can block CLI and SDK commands until a job enters a '
'specified state. By default, JobState.SUCCEEDED is used. See all '
'available states in the reference docs. CLI Python SDK anyscale job '
'wait -n job-wait When you submit a job, you can specify --wait, '
'which waits for the job to succeed or exits if the job fails. '
'anyscale job submit -n job-wait --wait -- sleep 30 For more '
'information on submitting jobs with the CLI, see the reference '
'docs. import anyscale\n'
'from anyscale.job.models import JobConfig\n'
'\n'
'config = JobConfig(name="job-wait", entrypoint="sleep 30")\n'
'\n'
'anyscale.job.submit(config)\n'
'anyscale.job.wait(name="job-wait") For more information on '
'submitting jobs with the SDK, see the reference docs. Terminating a '
'job\u200b You can terminate a job from the Job page or using the '
"CLI/SDK: CLI Python SDK anyscale job terminate --id 'prodjob_...' "
'For more information on terminating jobs with the CLI, see the '
'reference docs. import anyscale'},
{'chunk_id': 'f1e981ec-d129-49a0-8df6-86fc1da99d7f',
'chunk_index': 10,
'distance': 0.1282671093940735,
'doc_id': 'e747a479-126c-42ed-9f20-f84038229e7b',
'page_number': 1,
'score': 0.8717328906059265,
'source': 'anyscale-rag-application/100-docs/Monitor_a_job.docx',
'text': 'to look back. Anyscale stores up to 30 days of logs for your job. '
"You're able to debug issues even after the job terminates. To "
'filter the logs, use the search bar to search for specific '
'keywords. Enter a request ID in the search bar to filter logs for a '
'specific request. You can also use contain a specific pattern. '
'Alerts to filter logs if your logs Anyscale jobs have a built-in '
'alert for when a job succeeds or fails. The creator of the job '
'receives an email notification when the job completes. To set up '
'additional alerts based on your own criteria, see Custom dashboards '
'and alerting guide. These alerts are useful for tracking the health '
'of your jobs or job queues. Ray Dashboard The Ray Dashboard is '
'scoped to a single Ray cluster. Each job attempt launches a new Ray '
'cluster unless Job queues are used. To access this dashboard, click '
'the "Ray Dashboard" tab in the job detail page. To learn more about '
'how to use the Ray Dashboard, see the Ray documentation. Exporting '
'logs and metrics If you want to push logs to Vector, a tool to ship '
'logs to Amazon CloudWatch, Google Cloud Monitoring, Datadog, or '
'other observability tools, see Exporting logs and metrics with '
'Vector. More info To learn more details about the Ray Dashboard, '
'see the Ray Dashboard documentation To learn more about Grafana and '
'how to use it, see the official Grafana documentation To learn more '
'about the metrics that Ray emits, see the System Metrics '
'documentation'}]
Rendered Prompt:
('Use the following pieces of context to answer the question at the end.\n'
"If you don't know the answer, just say that you don't know, don't try to "
'make up an answer.\n'
'Use three sentences maximum and keep the answer as concise as possible.\n'
'Always say "thanks for asking!" at the end of the answer.\n'
'\n'
"[{'chunk_index': 1, 'chunk_id': '55b8db89-0aa6-460c-ae3a-284241f5865c', "
"'doc_id': '7b170e3d-4081-4527-a737-1da022a364c4', 'page_number': 1, "
"'source': 'anyscale-rag-application/100-docs/Jobs.txt', 'text': "
'"2/12/25, 9:48 AM Jobs | Anyscale Docs Jobs Run discrete workloads in '
'production such as batch inference, bulk embeddings generation, or model '
'fine-tuning. Anyscale Jobs allow you to submit applications developed on '
'workspaces to a standalone Ray cluster for execution. Built for production '
'and designed to fit into your CI/CD pipeline, jobs ensure scalable and '
'reliable performance. How does it work? # When you’re ready to promote an '
'app to production, submit a job from the workspace using anyscale job submit '
'. Anyscale Jobs have the following features: Scalability: Rapid scaling to '
'thousands of cloud instances, adjusting computing resources to match '
'application demand. Fault tolerance: Retries for failures and automatic '
'rescheduling to an alternative cluster for unexpected failures like running '
'out of memory. Monitoring and observability: Persistent dashboards that '
'allow you to observe tasks in real time and email alerts upon successf ul '
'job completion. Get started 1. Sign in or sign up for an account. 2. Select '
'the Intro to Jobs example. 3. Select Launch. This example runs in a '
'Workspace. See Workspaces for background information. 4. Follow the notebook '
"or view it in the docs. 5. Terminate the Workspace when you're done. Ask AI "
'https://docs.anyscale.com/platform/jobs/ 1/2 2/12/25, 9:48 AM Jobs | '
'Anyscale Docs https://docs.anyscale.com/platform/jobs/ 2/2", \'distance\': '
"0.10053980350494385, 'score': 0.8994601964950562}, {'chunk_index': 2, "
"'chunk_id': 'fdd75966-04d9-43d2-8e3e-b85e8387d086', 'doc_id': "
"'82efb8cd-2181-47cb-9389-ff101cc68674', 'page_number': 2, 'source': "
"'anyscale-rag-application/100-docs/Create_and_manage_jobs.pdf', 'text': "
"'2/12/25, 9:48 AM Create and manage jobs | Anyscale Docs Defining a job With "
'the CLI, you can define jobs in a YAML file and submit them by referencing '
'the YAML: anyscale job submit --config-file config.yaml For an example of '
'defining a job in a YAML, see the reference docs. Waiting on a job You can '
'block CLI and SDK commands until a job enters a specified state. By default, '
'JobState.SUCCEEDED is used. See all available states in the reference docs. '
'CLI Python SDK anyscale job wait -n job-wait When you submit a job, you can '
'specify --wait , which waits for the job to succeed or exits if the job '
'fails. anyscale job submit -n job-wait --wait -- sleep 30 For more '
'information on submitting jobs with the CLI, see the reference docs. '
'Terminating a job You can terminate a job from the Job page or using the '
'CLI/SDK: CLI Python SDK https://docs.anyscale.com/platform/jobs/manage-jobs '
"2/5', 'distance': 0.11302393674850464, 'score': 0.8869760632514954}, "
"{'chunk_index': 3, 'chunk_id': '23bf61db-155a-4a1a-a74f-669409c92303', "
"'doc_id': '91ddd49b-9e23-4e58-9143-bbac61ee2157', 'page_number': 1, "
"'source': 'anyscale-rag-application/100-docs/Job_schedules.html', 'text': "
'\'anyscale.job.terminate(name="my-job") For more information on terminating '
'jobs with the SDK, see the reference docs. Archiving a job\\u200b Archiving '
'jobs hide them from the job list page, but you can still access them through '
'the CLI and SDK. The cluster associated with an archived job is archived '
'automatically. To be archived, jobs must be in a terminal state. You must '
'have created the job or be an organization admin to archive the job. You can '
'archive jobs in Anyscale console or through the CLI/SDK: CLI Python SDK '
"anyscale job archive --id \\'prodjob_...\\' For more information on "
'archiving jobs with the CLI, see the reference docs. import '
'anyscale\\n\\nanyscale.job.archive(name="my-job") For more information on '
'archiving jobs with the SDK, see the reference docs. Managing '
'dependencies\\u200b When developing Anyscale jobs, you may need to include '
'additional Python packages or system-level dependencies. There are several '
'ways to manage these dependencies: Using a requirements.txt file\\u200b The '
'simplest way to manage Python package dependencies is by using a '
'requirements.txt file. Create a requirements.txt file in your project '
'directory: emoji==2.12.1\\nnumpy==1.21.0 When submitting your job, include '
'the -r or --requirements flag: CLI Python SDK anyscale job submit '
'--config-file job.yaml -r ./requirements.txt import anyscale\\nfrom '
'anyscale.job.models import JobConfig\\n\\nconfig = JobConfig(\\n '
'name="my-job",\\n entrypoint="python main.py",\\n '
'working_dir=".",\\n '
'requirements="./requirements.txt"\\n)\\n\\nanyscale.job.submit(config) This '
'method works well for straightforward Python package dependencies. Anyscale '
"installs these packages in the job\\'s environment before running your code. "
'Using a custom container\\u200b For more complex dependency management, '
'including system-level packages or specific environment configurations, use '
'a custom container: Create a Dockerfile: FROM '
'anyscale/ray:2.10.0-py310\\n\\n# Install system dependencies if needed\\nRUN '
"apt-get update && apt-get install -y <your-system-packages>', 'distance': "
"0.11444741487503052, 'score': 0.8855525851249695}, {'chunk_index': 4, "
"'chunk_id': '13683649-bcdc-444d-866f-36cafcb132c9', 'doc_id': "
"'91ddd49b-9e23-4e58-9143-bbac61ee2157', 'page_number': 1, 'source': "
"'anyscale-rag-application/100-docs/Job_schedules.html', 'text': 'Create and "
'manage jobs Submitting a job\\u200b To submit your job to Anyscale, use the '
'Python SDK or CLI and pass in any additional options or configurations for '
'the job. By default, Anyscale uses your workspace or cloud to provision a '
'cluster to run your job. You can define a custom cluster through a compute '
'config or specify an existing cluster. Once submitted, Anyscale runs the job '
'as specified in the entrypoint command, which is typically a Ray Job. If the '
"run doesn\\'t succeed, the job restarts using the same entrypoint up to the "
'number of max_retries. CLI Python SDK anyscale job submit --name=my-job '
'\\\\\\n --working-dir=. --max-retries=5 \\\\\\n '
'--image-uri="anyscale/image/IMAGE_NAME:VERSION" \\\\\\n '
'--compute-config=COMPUTE_CONFIG_NAME \\\\\\n -- python main.py With the '
'CLI, you can either specify an existing compute config with '
'--compute-config=COMPUTE_CONFIG_NAME or define a new one in a job YAML. For '
'more information on submitting jobs with the CLI, see the reference docs. '
'import anyscale\\nfrom anyscale.job.models import JobConfig\\n\\nconfig = '
'JobConfig(\\n name="my-job",\\n entrypoint="python main.py",\\n '
'working_dir=".",\\n max_retries=5,\\n '
'image_uri="anyscale/image/IMAGE_NAME:VERSION",\\n '
'compute_config="COMPUTE_CONFIG_NAME"\\n)\', \'distance\': '
"0.11574643850326538, 'score': 0.8842535614967346}, {'chunk_index': 5, "
"'chunk_id': '3167ba0b-2aff-4f69-8dbe-7a8cdc725005', 'doc_id': "
"'7a7730fa-96a1-4775-896a-11deac94d668', 'page_number': 1, 'source': "
"'anyscale-rag-application/100-docs/Job_queues.pptx', 'text': '2/12/25, 9:48 "
'AM\\tJob queues | Anyscale Docs Job queues A job queue enables sophisticated '
'scheduling and execution algorithms for Anyscale Jobs. This feature improves '
'resource utilization and reduces provisioning times by enabling multiple '
'jobs to share a single cluster. Anyscale supports flexible scheduling '
'algorithms, including FIFO (first-in, first-out), LIFO (last-in, first-out), '
'and priority-based scheduling. Job processing Anyscale job queues optimize '
'resource utilization and throughput by using sophisticated scheduling to run '
'multiple jobs on the same cluster. Submission: The typical Anyscale Job '
'submission workflow adds the job to the specified queue. Scheduling: Based '
'on the scheduling policy, Anyscale determines ordering of the jobs in the '
'queue and picks jobs at the top of the queue for scheduling. Anyscale '
'schedules no more than the specified max-concurrency jobs for running on a '
'cluster at the same time. Execution: Jobs run until completion, including '
'retries up to the specified number of max_retries . Anyscale provisions a '
'cluster when you submit the first job in a queue, and continues running '
'until there are no more jobs in the queue and it idles. Create a job queue '
'Creating a job queue is similar to creating a standalone Anyscale Job. In '
'your job.yaml file, specify additional job queue configurations: '
'CLI\\tPython SDK Ask AI https://docs.anyscale.com/platform/jobs/job-queues '
"1/5', 'distance': 0.11749774217605591, 'score': 0.8825022578239441}, "
"{'chunk_index': 6, 'chunk_id': '8c158e24-22e2-4984-a402-2331cf0896fc', "
"'doc_id': '82efb8cd-2181-47cb-9389-ff101cc68674', 'page_number': 1, "
"'source': 'anyscale-rag-application/100-docs/Create_and_manage_jobs.pdf', "
"'text': '2/12/25, 9:48 AM Create and manage jobs | Anyscale Docs Create and "
'manage jobs Submitting a job To submit your job to Anyscale, use the Python '
'SDK or CLI and pass in any additional options or configurations for the job. '
'By default, Anyscale uses your workspace or cloud to provision a cluster to '
'run your job. You can define a custom cluster through a compute config or '
'specify an existing cluster. Once submitted, Anyscale runs the job as '
'specified in the entrypoint command, which is typically a Ray Job. If the '
"run doesn\\'t succeed, the job restarts using the same entrypoint up to the "
'number of max_retries . CLI Python SDK anyscale job submit --name=my-job '
'\\\\ --working-dir=. --max-retries=5 \\\\ '
'--image-uri="anyscale/image/IMAGE_NAME:VERSION" \\\\ '
'--compute-config=COMPUTE_CONFIG_NAME \\\\ -- python main.py With the CLI, '
'you can either specify an existing compute config with --compute- '
'config=COMPUTE_CONFIG_NAME or define a new one in a job YAML. For more '
'information on submitting jobs with the CLI, see the reference docs. TIP For '
'large-scale, compute-intensive jobs, avoid scheduling Ray tasks onto the '
'head node because it manages cluster-level orchestration. To do that, set '
'the CPU resource on the head node to 0 in your compute config. Ask AI '
"https://docs.anyscale.com/platform/jobs/manage-jobs 1/5', 'distance': "
"0.12043756246566772, 'score': 0.8795624375343323}, {'chunk_index': 7, "
"'chunk_id': '2d0623d0-911f-471a-9649-a61c0b2db411', 'doc_id': "
"'82efb8cd-2181-47cb-9389-ff101cc68674', 'page_number': 5, 'source': "
"'anyscale-rag-application/100-docs/Create_and_manage_jobs.pdf', 'text': "
"'2/12/25, 9:48 AM Create and manage jobs | Anyscale Docs Using pre-built "
'custom images For frequently used environments, you can build and reuse '
'custom images: 1. Build the image: CLI Python SDK anyscale image build -n '
'my-custom-image --containerfile Dockerfile 2. Use the built image in your '
'job submission: CLI Python SDK anyscale job submit --config-file job.yaml '
'--image-uri anyscale/image/my- custom-image:1 This approach is efficient for '
'teams working on multiple jobs that share the same dependencies. '
"https://docs.anyscale.com/platform/jobs/manage-jobs 5/5', 'distance': "
"0.12314975261688232, 'score': 0.8768502473831177}, {'chunk_index': 8, "
"'chunk_id': '96285d69-2f27-4fb6-81be-31a4ededffba', 'doc_id': "
"'82efb8cd-2181-47cb-9389-ff101cc68674', 'page_number': 3, 'source': "
"'anyscale-rag-application/100-docs/Create_and_manage_jobs.pdf', 'text': "
'"2/12/25, 9:48 AM Create and manage jobs | Anyscale Docs anyscale job '
"terminate --id 'prodjob_...' For more information on terminating jobs with "
'the CLI, see the reference docs. Archiving a job Archiving jobs hide them '
'from the job list page, but you can still access them through the CLI and '
'SDK. The cluster associated with an archived job is archived automatically. '
'To be archived, jobs must be in a terminal state. You must have created the '
'job or be an organization admin to archive the job. You can archive jobs in '
'Anyscale console or through the CLI/SDK: CLI Python SDK anyscale job archive '
"--id 'prodjob_...' For more information on archiving jobs with the CLI, see "
'the reference docs. Managing dependencies When developing Anyscale jobs, you '
'may need to include additional Python packages or system- level '
'dependencies. There are several ways to manage these dependencies: Using a '
'requirements.txt file The simplest way to manage Python package dependencies '
'is by using a requirements.txt file. 1. Create a requirements.txt file in '
'your project directory: emoji==2.12.1 numpy==1.21.0 '
'https://docs.anyscale.com/platform/jobs/manage-jobs 3/5", \'distance\': '
"0.1248595118522644, 'score': 0.8751404881477356}, {'chunk_index': 9, "
"'chunk_id': 'd7c57ead-0228-4c49-bb77-37b67aed463d', 'doc_id': "
"'91ddd49b-9e23-4e58-9143-bbac61ee2157', 'page_number': 1, 'source': "
"'anyscale-rag-application/100-docs/Job_schedules.html', 'text': 'config = "
'JobConfig(\\n name="my-job",\\n entrypoint="python main.py",\\n '
'working_dir=".",\\n max_retries=5,\\n '
'image_uri="anyscale/image/IMAGE_NAME:VERSION",\\n '
'compute_config="COMPUTE_CONFIG_NAME"\\n)\\n\\nanyscale.job.submit(config) '
'With the SDK, you can either specify an existing compute config or define a '
'new one using the compute config API. For more information on submitting '
'jobs with the SDK, see the reference docs. For a complete list of supported '
'options defining a JobConfig, see the reference docs for JobConfig. tip For '
'large-scale, compute-intensive jobs, avoid scheduling Ray tasks onto the '
'head node because it manages cluster-level orchestration. To do that, set '
'the CPU resource on the head node to 0 in your compute config. Defining a '
'job\\u200b With the CLI, you can define jobs in a YAML file and submit them '
'by referencing the YAML: anyscale job submit --config-file config.yaml For '
'an example of defining a job in a YAML, see the reference docs. Waiting on a '
'job\\u200b You can block CLI and SDK commands until a job enters a specified '
'state. By default, JobState.SUCCEEDED is used. See all available states in '
'the reference docs. CLI Python SDK anyscale job wait -n job-wait When you '
'submit a job, you can specify --wait, which waits for the job to succeed or '
'exits if the job fails. anyscale job submit -n job-wait --wait -- sleep 30 '
'For more information on submitting jobs with the CLI, see the reference '
'docs. import anyscale\\nfrom anyscale.job.models import '
'JobConfig\\n\\nconfig = JobConfig(name="job-wait", entrypoint="sleep '
'30")\\n\\nanyscale.job.submit(config)\\nanyscale.job.wait(name="job-wait") '
'For more information on submitting jobs with the SDK, see the reference '
'docs. Terminating a job\\u200b You can terminate a job from the Job page or '
'using the CLI/SDK: CLI Python SDK anyscale job terminate --id '
"\\'prodjob_...\\' For more information on terminating jobs with the CLI, see "
"the reference docs. import anyscale', 'distance': 0.12725389003753662, "
"'score': 0.8727461099624634}, {'chunk_index': 10, 'chunk_id': "
"'f1e981ec-d129-49a0-8df6-86fc1da99d7f', 'doc_id': "
"'e747a479-126c-42ed-9f20-f84038229e7b', 'page_number': 1, 'source': "
"'anyscale-rag-application/100-docs/Monitor_a_job.docx', 'text': 'to look "
"back. Anyscale stores up to 30 days of logs for your job. You\\'re able to "
'debug issues even after the job terminates. To filter the logs, use the '
'search bar to search for specific keywords. Enter a request ID in the search '
'bar to filter logs for a specific request. You can also use contain a '
'specific pattern. Alerts to filter logs if your logs Anyscale jobs have a '
'built-in alert for when a job succeeds or fails. The creator of the job '
'receives an email notification when the job completes. To set up additional '
'alerts based on your own criteria, see Custom dashboards and alerting guide. '
'These alerts are useful for tracking the health of your jobs or job queues. '
'Ray Dashboard The Ray Dashboard is scoped to a single Ray cluster. Each job '
'attempt launches a new Ray cluster unless Job queues are used. To access '
'this dashboard, click the "Ray Dashboard" tab in the job detail page. To '
'learn more about how to use the Ray Dashboard, see the Ray documentation. '
'Exporting logs and metrics If you want to push logs to Vector, a tool to '
'ship logs to Amazon CloudWatch, Google Cloud Monitoring, Datadog, or other '
'observability tools, see Exporting logs and metrics with Vector. More info '
'To learn more details about the Ray Dashboard, see the Ray Dashboard '
'documentation To learn more about Grafana and how to use it, see the '
'official Grafana documentation To learn more about the metrics that Ray '
"emits, see the System Metrics documentation', 'distance': "
"0.1282671093940735, 'score': 0.8717328906059265}]\n"
'\n'
'Question: what is a anyscale job\n'
'\n'
'Helpful Answer:')
获取最终响应#
使用生成的提示流式传输 LLM 的响应。
for token in client.get_response_streaming(prompt, temperature=0.5):
print(token, end="")
Anyscale Jobs are used to run discrete workloads in production, such as batch inference or model fine-tuning, on a standalone Ray cluster for scalable and reliable performance. Thanks for asking!
观察与后续步骤#
如您所见,LLM 现在明白了 Anysacle jobs 指的是平台,而不是 Anysacale 的职位空缺。这证明了使用 RAG 的强大功能。然而,这个基础 RAG 实现的响应并非最优:它太简短,缺乏引用,让我们不清楚信息的来源。在未来的教程中,我们将评估这些问题,并通过提示工程提出几种解决方法。