分布式 XGBoost 模型训练#
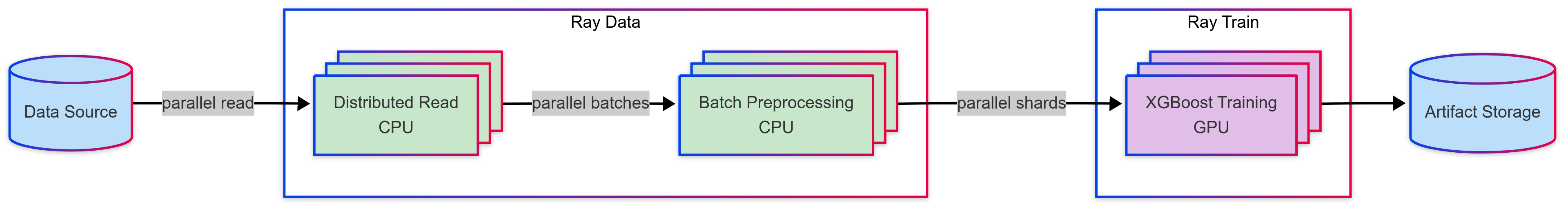
本教程将执行一个分布式训练工作负载,该工作负载连接了以下具有异构计算需求的步骤:
使用 Ray Data 预处理数据集
使用 Ray Train 分布式训练 XGBoost 模型
使用 MLflow 将模型构件保存到模型注册表
注意:本教程不包括模型调优。有关实验执行和超参数调优,请参阅 Ray Tune。
依赖项#
要安装依赖项,请运行以下命令:
pip install -r requirements.txt
设置#
导入必要的模块
%load_ext autoreload
%autoreload all
# Enable importing from dist_xgboost module.
import os
import sys
sys.path.append(os.path.abspath(".."))
# Enable Ray Train v2. This is the default in an upcoming release.
os.environ["RAY_TRAIN_V2_ENABLED"] = "1"
# Now it's safe to import from ray.train
import ray
from dist_xgboost.constants import storage_path, preprocessor_path
# Make Ray data less verbose.
ray.data.DataContext.get_current().enable_progress_bars = False
ray.data.DataContext.get_current().print_on_execution_start = False
数据集准备#
本示例使用了 Breast Cancer Wisconsin (Diagnostic) 数据集,该数据集包含从乳腺肿块细胞核数字化图像计算出的特征。
将数据拆分为
70% 用于训练
15% 用于验证
15% 用于测试
from ray.data import Dataset
def prepare_data() -> tuple[Dataset, Dataset, Dataset]:
"""Load and split the dataset into train, validation, and test sets."""
# Load the dataset from S3.
dataset = ray.data.read_csv("s3://anonymous@air-example-data/breast_cancer.csv")
seed = 42
# Split 70% for training.
train_dataset, rest = dataset.train_test_split(test_size=0.3, shuffle=True, seed=seed)
# Split the remaining 30% into 15% validation and 15% testing.
valid_dataset, test_dataset = rest.train_test_split(test_size=0.5, shuffle=True, seed=seed)
return train_dataset, valid_dataset, test_dataset
# Load and split the dataset.
train_dataset, valid_dataset, _test_dataset = prepare_data()
train_dataset.take(1)
2025-04-16 21:01:53,956 INFO worker.py:1660 -- Connecting to existing Ray cluster at address: 10.0.23.200:6379...
2025-04-16 21:01:53,966 INFO worker.py:1843 -- Connected to Ray cluster. View the dashboard at https://session-1kebpylz8tcjd34p4sv2h1f9tg.i.anyscaleuserdata.com
2025-04-16 21:01:53,972 INFO packaging.py:575 -- Creating a file package for local module '/home/ray/default/e2e-xgboost/dist_xgboost'.
2025-04-16 21:01:53,975 INFO packaging.py:367 -- Pushing file package 'gcs://_ray_pkg_aa0e5fd0ec6b8edc.zip' (0.02MiB) to Ray cluster...
2025-04-16 21:01:53,976 INFO packaging.py:380 -- Successfully pushed file package 'gcs://_ray_pkg_aa0e5fd0ec6b8edc.zip'.
2025-04-16 21:01:53,977 INFO packaging.py:367 -- Pushing file package 'gcs://_ray_pkg_38ec1ca756a7ccf23a0c590d356f26fc87860d8a.zip' (0.07MiB) to Ray cluster...
2025-04-16 21:01:53,978 INFO packaging.py:380 -- Successfully pushed file package 'gcs://_ray_pkg_38ec1ca756a7ccf23a0c590d356f26fc87860d8a.zip'.
(autoscaler +11s) Tip: use `ray status` to view detailed cluster status. To disable these messages, set RAY_SCHEDULER_EVENTS=0.
(autoscaler +11s) [autoscaler] [8CPU-32GB] Attempting to add 1 node(s) to the cluster (increasing from 0 to 1).
(autoscaler +11s) [autoscaler] [8CPU-32GB] Launched 1 instances.
2025-04-16 21:03:12,957 INFO dataset.py:2809 -- Tip: Use `take_batch()` instead of `take() / show()` to return records in pandas or numpy batch format.
[{'mean radius': 19.16,
'mean texture': 26.6,
'mean perimeter': 126.2,
'mean area': 1138.0,
'mean smoothness': 0.102,
'mean compactness': 0.1453,
'mean concavity': 0.1921,
'mean concave points': 0.09664,
'mean symmetry': 0.1902,
'mean fractal dimension': 0.0622,
'radius error': 0.6361,
'texture error': 1.001,
'perimeter error': 4.321,
'area error': 69.65,
'smoothness error': 0.007392,
'compactness error': 0.02449,
'concavity error': 0.03988,
'concave points error': 0.01293,
'symmetry error': 0.01435,
'fractal dimension error': 0.003446,
'worst radius': 23.72,
'worst texture': 35.9,
'worst perimeter': 159.8,
'worst area': 1724.0,
'worst smoothness': 0.1782,
'worst compactness': 0.3841,
'worst concavity': 0.5754,
'worst concave points': 0.1872,
'worst symmetry': 0.3258,
'worst fractal dimension': 0.0972,
'target': 0}]
查看输出,您会发现数据集中包含表征乳腺肿块细胞核的特征,例如半径、纹理、周长、面积、光滑度、紧凑度、凹度、对称性等。
数据预处理#
请注意,这些特征的量级和范围各不相同。虽然像 XGBoost 这样的基于树的模型对这些差异不太敏感,但在某些情况下,特征缩放仍然可以提高数值稳定性。
Ray Data 具有内置的预处理器,可以简化常见的特征预处理任务,尤其适用于表格数据。您可以将这些预处理器与 Ray Datasets 集成,以容错和分布式的方式进行数据预处理。
本示例使用 Ray 的内置 StandardScaler 来零均值化和标准化特征。
from ray.data.preprocessors import StandardScaler
def train_preprocessor(train_dataset: ray.data.Dataset) -> StandardScaler:
# Pick some dataset columns to scale.
columns_to_scale = [c for c in train_dataset.columns() if c != "target"]
# Initialize the preprocessor.
preprocessor = StandardScaler(columns=columns_to_scale)
# Train the preprocessor on the training set.
preprocessor.fit(train_dataset)
return preprocessor
preprocessor = train_preprocessor(train_dataset)
现在您已经拟合了预处理器,将其保存到文件中。稍后在 MLflow 中注册此构件,以便在下游管道中重复使用。
import pickle
with open(preprocessor_path, "wb") as f:
pickle.dump(preprocessor, f)
接下来,使用拟合的预处理器转换数据集。请注意,transform() 操作是惰性的。Ray Data 不会立即将其应用于数据,直到 Ray Train 工作进程需要数据为止。
train_dataset = preprocessor.transform(train_dataset)
valid_dataset = preprocessor.transform(valid_dataset)
train_dataset.take(1)
[{'mean radius': 1.3883915483364895,
'mean texture': 1.6582900738074817,
'mean perimeter': 1.3686612092802328,
'mean area': 1.3271629358408426,
'mean smoothness': 0.3726369329455741,
'mean compactness': 0.7709391453349583,
'mean concavity': 1.2156484038771678,
'mean concave points': 1.1909841981870102,
'mean symmetry': 0.33295997290846857,
'mean fractal dimension': -0.07207903519571106,
'radius error': 0.8074600624242092,
'texture error': -0.3842391069975234,
'perimeter error': 0.6925593054563496,
'area error': 0.5852832746827147,
'smoothness error': 0.13331319500721583,
'compactness error': -0.03934175265392654,
'concavity error': 0.22009334597724586,
'concave points error': 0.16570998568362863,
'symmetry error': -0.7220900323187186,
'fractal dimension error': -0.13670701917436776,
'worst radius': 1.5076654048043645,
'worst texture': 1.6169142713721316,
'worst perimeter': 1.5267353447826646,
'worst area': 1.4332237868207693,
'worst smoothness': 1.993402211865443,
'worst compactness': 0.8646836438651355,
'worst concavity': 1.3882655471454963,
'worst concave points': 1.0898377217385602,
'worst symmetry': 0.5707716568830431,
'worst fractal dimension': 0.7444861349012516,
'target': 0}]
使用 take(),您会看到 Ray Data 已零均值化并重缩放了值,使其大致在 -1 和 1 之间。
数据处理说明:
有关更高级的数据加载和预处理技术,请参阅 综合指南。如果需要,Ray Data 还支持高性能的连接、过滤、聚合和其他操作,以进行更结构化的数据处理。
使用 XGBoost 进行模型训练#
检查点配置#
检查点是一项强大的功能,可在中断时从最后一个检查点恢复训练。检查点对于长时间运行的训练会话尤其有用。
XGBoostTrainer 开箱即用地实现了检查点功能。通过配置 CheckpointConfig 来设置检查点频率。
from ray.train import CheckpointConfig, Result, RunConfig, ScalingConfig
# Configure checkpointing to save progress during training.
run_config = RunConfig(
checkpoint_config=CheckpointConfig(
# Checkpoint every 10 iterations.
checkpoint_frequency=10,
# Only keep the latest checkpoint.
num_to_keep=1,
),
## For multi-node clusters, configure storage that's accessible
## across all worker nodes with `storage_path="s3://..."`.
storage_path=storage_path,
)
注意:启用检查点后,您可以按照 本指南 来启用容错。
使用 XGBoost 进行训练#
将训练参数作为字典传递,类似于原始的 xgboost.train() 函数。
import xgboost
from ray.train.xgboost import RayTrainReportCallback, XGBoostTrainer
NUM_WORKERS = 4
USE_GPU = True
def train_fn_per_worker(config: dict):
"""Training function that runs on each worker.
This function:
1. Gets the dataset shard for this worker
2. Converts to pandas for XGBoost
3. Separates features and labels
4. Creates DMatrix objects
5. Trains the model using distributed communication
"""
# Get this worker's dataset shard.
train_ds, val_ds = (
ray.train.get_dataset_shard("train"),
ray.train.get_dataset_shard("validation"),
)
# Materialize the data and convert to pandas.
train_ds = train_ds.materialize().to_pandas()
val_ds = val_ds.materialize().to_pandas()
# Separate the labels from the features.
train_X, train_y = train_ds.drop("target", axis=1), train_ds["target"]
eval_X, eval_y = val_ds.drop("target", axis=1), val_ds["target"]
# Convert the data into DMatrix format for XGBoost.
dtrain = xgboost.DMatrix(train_X, label=train_y)
deval = xgboost.DMatrix(eval_X, label=eval_y)
# Do distributed data-parallel training.
# Ray Train sets up the necessary coordinator processes and
# environment variables for workers to communicate with each other.
_booster = xgboost.train(
config["xgboost_params"],
dtrain=dtrain,
evals=[(dtrain, "train"), (deval, "validation")],
num_boost_round=10,
# Handles metric logging and checkpointing.
callbacks=[RayTrainReportCallback()],
)
# Parameters for the XGBoost model.
model_config = {
"xgboost_params": {
"objective": "binary:logistic",
"eval_metric": ["logloss", "error"],
}
}
trainer = XGBoostTrainer(
train_fn_per_worker,
train_loop_config=model_config,
# Register the data subsets.
datasets={"train": train_dataset, "validation": valid_dataset},
# See "Scaling strategies" for more details.
scaling_config=ScalingConfig(
# Number of workers for data parallelism.
num_workers=NUM_WORKERS,
# Set to True to use GPU acceleration.
use_gpu=USE_GPU,
),
run_config=run_config,
)
Ray Train 的优势:
多节点编排:自动处理多节点、多 GPU 设置,无需手动 SSH 或 hostfile 配置。
内置容错:支持自动重试失败的工作进程,并可从最后一个检查点继续。
灵活的训练策略:支持除数据并行训练以外的各种并行策略。
异构集群支持:定义每个工作进程的资源需求,并在混合硬件上运行。
Ray Train 与 PyTorch、TensorFlow、XGBoost 等流行框架集成。对于企业级需求,RayTurbo Train 提供了弹性训练、高级监控和性能优化等附加功能。

接下来,训练模型。
result: Result = trainer.fit()
result
(TrainController pid=19121) Attempting to start training worker group of size 5 with the following resources: [{'GPU': 1}] * 5
(autoscaler +1m31s) [autoscaler] [8xA10G:192CPU-768GB] Attempting to add 1 node(s) to the cluster (increasing from 0 to 1).
(autoscaler +1m31s) [autoscaler] Launching instances failed: NewInstances[g5.48xlarge;num:1;all:false]: could not launch any instances: api error Unsupported: Instance type g5.48xlarge is not supported in zone us-west-2d.
(autoscaler +1m31s) [autoscaler] [1xA10G:16CPU-64GB] Attempting to add 5 node(s) to the cluster (increasing from 0 to 5).
(autoscaler +1m31s) [autoscaler] Launching instances failed: NewInstances[g5.4xlarge;num:5;all:false]: could not launch any instances: api error Unsupported: Instance type g5.4xlarge is not supported in zone us-west-2d.
(autoscaler +1m31s) [autoscaler] [1xA10G:32CPU-128GB] Attempting to add 5 node(s) to the cluster (increasing from 0 to 5).
(autoscaler +1m36s) [autoscaler] Launching instances failed: NewInstances[g5.8xlarge;num:5;all:false]: could not launch any instances: api error Unsupported: Instance type g5.8xlarge is not supported in zone us-west-2d.
(autoscaler +1m36s) [autoscaler] [1xL4:4CPU-16GB] Attempting to add 1 node(s) to the cluster (increasing from 0 to 1).
(autoscaler +1m36s) [autoscaler] [4xL4:48CPU-192GB] Attempting to add 1 node(s) to the cluster (increasing from 0 to 1).
(autoscaler +1m36s) [autoscaler] [4xL4:48CPU-192GB] Launched 1 instances.
(autoscaler +1m36s) [autoscaler] [1xL4:4CPU-16GB] Launched 1 instances.
(TrainController pid=19121) Retrying the launch of the training worker group. The previous launch attempt encountered the following failure:
(TrainController pid=19121) The worker group startup timed out after 30.0 seconds waiting for 5 workers. Potential causes include: (1) temporary insufficient cluster resources while waiting for autoscaling (ignore this warning in this case), (2) infeasible resource request where the provided `ScalingConfig` cannot be satisfied), and (3) transient network issues. Set the RAY_TRAIN_WORKER_GROUP_START_TIMEOUT_S environment variable to increase the timeout.
(TrainController pid=19121) Attempting to start training worker group of size 5 with the following resources: [{'GPU': 1}] * 5
(autoscaler +2m21s) [autoscaler] Cluster upscaled to {12 CPU, 1 GPU}.
(TrainController pid=19121) Retrying the launch of the training worker group. The previous launch attempt encountered the following failure:
(TrainController pid=19121) The worker group startup timed out after 30.0 seconds waiting for 5 workers. Potential causes include: (1) temporary insufficient cluster resources while waiting for autoscaling (ignore this warning in this case), (2) infeasible resource request where the provided `ScalingConfig` cannot be satisfied), and (3) transient network issues. Set the RAY_TRAIN_WORKER_GROUP_START_TIMEOUT_S environment variable to increase the timeout.
(TrainController pid=19121) Attempting to start training worker group of size 5 with the following resources: [{'GPU': 1}] * 5
(autoscaler +2m31s) [autoscaler] Cluster upscaled to {60 CPU, 5 GPU}.
(raylet) WARNING: 4 PYTHON worker processes have been started on node: dc30e171b93f61245644ba4d0147f8b27f64e9e1eaf34d1bb63c9c99 with address: 10.0.23.200. This could be a result of using a large number of actors, or due to tasks blocked in ray.get() calls (see https://github.com/ray-project/ray/issues/3644 for some discussion of workarounds).
(RayTrainWorker pid=3285, ip=10.0.223.105) [21:04:38] Task [xgboost.ray-rank=00000002]:fa43387771ebd5738fd50b6303000000 got rank 2
(TrainController pid=19121) [21:04:42] [0] train-logloss:0.44514 train-error:0.04051 validation-logloss:0.43997 validation-error:0.04706
(TrainController pid=19121) [21:04:44] [1] train-logloss:0.31649 train-error:0.01772 validation-logloss:0.31594 validation-error:0.04706
(RayTrainWorker pid=2313, ip=10.0.223.33) [21:04:38] Task [xgboost.ray-rank=00000004]:a6ed8004330660f5a370531f03000000 got rank 4 [repeated 4x across cluster] (Ray deduplicates logs by default. Set RAY_DEDUP_LOGS=0 to disable log deduplication, or see https://docs.rayai.org.cn/en/master/ray-observability/user-guides/configure-logging.html#log-deduplication for more options.)
(TrainController pid=19121) [21:04:46] [2] train-logloss:0.23701 train-error:0.01266 validation-logloss:0.24072 validation-error:0.02353
(TrainController pid=19121) [21:04:48] [3] train-logloss:0.18165 train-error:0.00759 validation-logloss:0.19038 validation-error:0.01176
(TrainController pid=19121) [21:04:50] [4] train-logloss:0.14258 train-error:0.00759 validation-logloss:0.14917 validation-error:0.01176
(TrainController pid=19121) [21:04:52] [5] train-logloss:0.11360 train-error:0.00759 validation-logloss:0.12113 validation-error:0.01176
(TrainController pid=19121) [21:04:54] [6] train-logloss:0.09207 train-error:0.00759 validation-logloss:0.10018 validation-error:0.01176
(TrainController pid=19121) [21:04:56] [7] train-logloss:0.07616 train-error:0.00506 validation-logloss:0.08632 validation-error:0.01176
(TrainController pid=19121) [21:04:58] [8] train-logloss:0.06419 train-error:0.00506 validation-logloss:0.07705 validation-error:0.01176
(TrainController pid=19121) [21:05:00] [9] train-logloss:0.05463 train-error:0.00506 validation-logloss:0.06741 validation-error:0.01176
(RayTrainWorker pid=3284, ip=10.0.223.105) Checkpoint successfully created at: Checkpoint(filesystem=local, path=/mnt/user_storage/ray_train_run-2025-04-16_21-03-13/checkpoint_2025-04-16_21-05-00.160991)
Result(metrics=OrderedDict({'train-logloss': 0.05463397157248817, 'train-error': 0.00506329113924051, 'validation-logloss': 0.06741214815308066, 'validation-error': 0.01176470588235294}), checkpoint=Checkpoint(filesystem=local, path=/mnt/user_storage/ray_train_run-2025-04-16_21-03-13/checkpoint_2025-04-16_21-05-00.160991), error=None, path='/mnt/user_storage/ray_train_run-2025-04-16_21-03-13', metrics_dataframe= train-logloss train-error validation-logloss validation-error
0 0.054634 0.005063 0.067412 0.011765, best_checkpoints=[(Checkpoint(filesystem=local, path=/mnt/user_storage/ray_train_run-2025-04-16_21-03-13/checkpoint_2025-04-16_21-05-00.160991), OrderedDict({'train-logloss': 0.05463397157248817, 'train-error': 0.00506329113924051, 'validation-logloss': 0.06741214815308066, 'validation-error': 0.01176470588235294}))], _storage_filesystem=<pyarrow._fs.LocalFileSystem object at 0x7ea450adb130>)
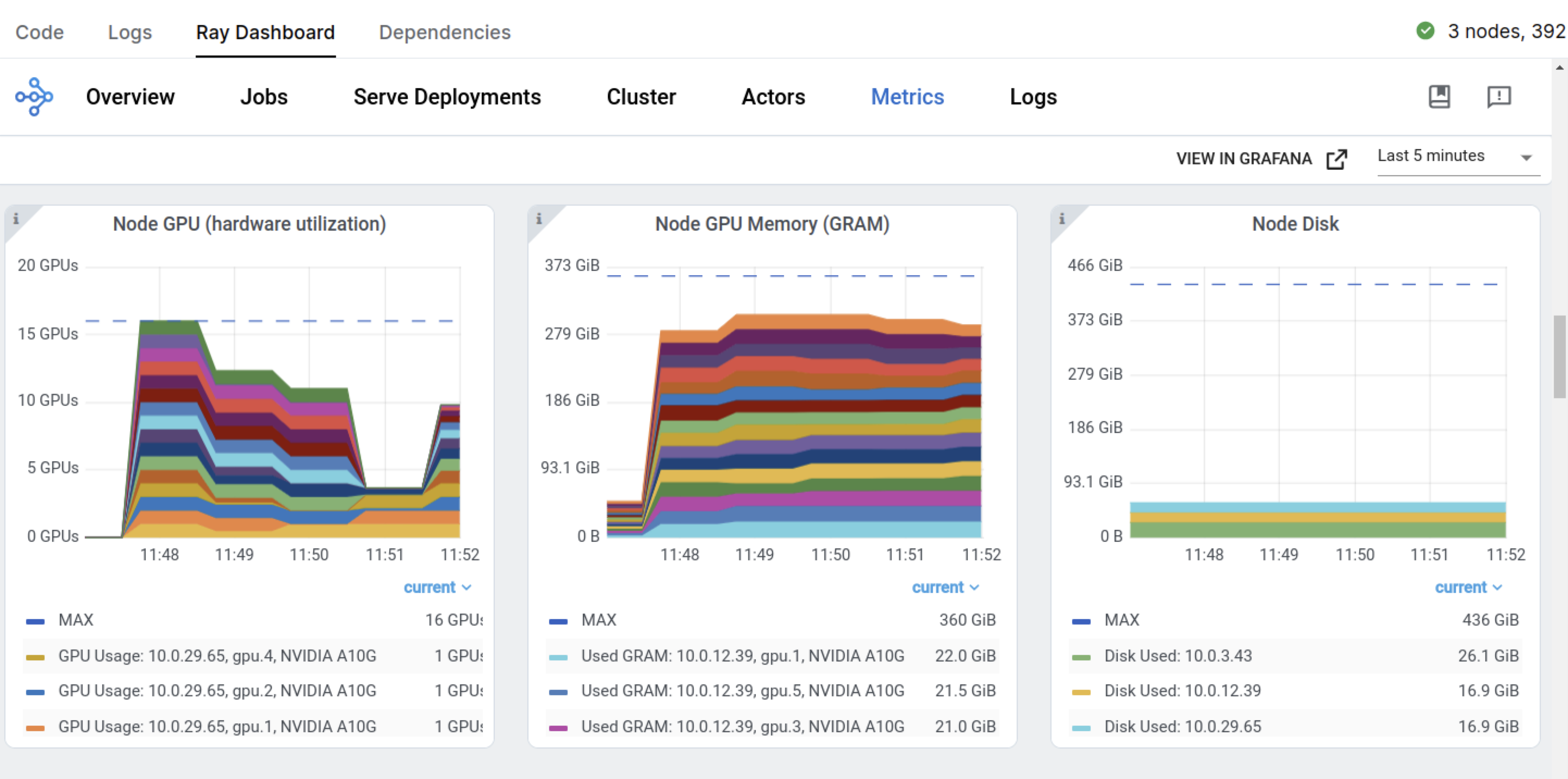
在训练作业开始时,Ray 开始请求 GPU 节点,以满足训练作业对五个 GPU 工作进程的需求。
Ray Train 返回一个 ray.train.Result 对象,其中包含重要的属性,如指标、检查点信息和错误详细信息。
metrics = result.metrics
metrics
OrderedDict([('train-logloss', 0.05463397157248817),
('train-error', 0.00506329113924051),
('validation-logloss', 0.06741214815308066),
('validation-error', 0.01176470588235294)])
预期的输出类似于以下内容:
OrderedDict([('train-logloss', 0.05463397157248817),
('train-error', 0.00506329113924051),
('validation-logloss', 0.06741214815308066),
('validation-error', 0.01176470588235294)])
可以看到,Ray Train 根据您在 eval_metric 和 evals 中配置的值记录了指标。
您还可以从检查点目录中重建训练好的模型。
booster = RayTrainReportCallback.get_model(result.checkpoint)
booster
<xgboost.core.Booster at 0x7ea4531beea0>
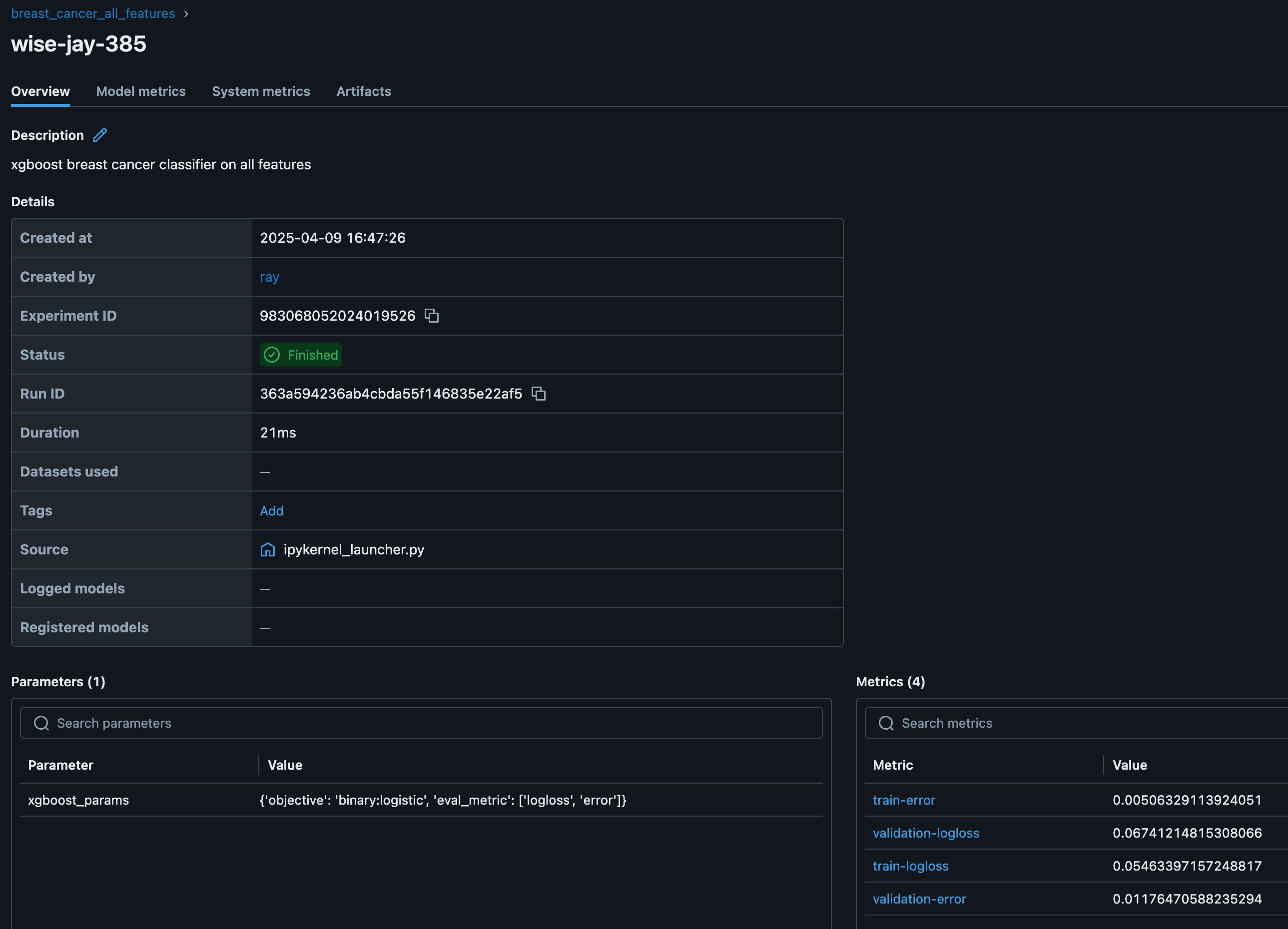
模型注册表#
训练好模型后,将其保存到模型注册表以供将来使用。由于这是一个分布式训练工作负载,模型注册表存储需要从集群中的所有工作进程中可访问。此存储可以是 S3、NFS 或其他网络附加解决方案。Anyscale 通过在每个集群节点上自动创建和挂载 共享存储选项 来简化此过程,确保模型构件在分布式环境中可读写。
MLflow 跟踪服务器将实验元数据和模型构件存储在共享存储位置,以便将来进行模型服务、评估或重新训练。Ray 还与其他 实验跟踪器 集成。
import shutil
from tempfile import TemporaryDirectory
import mlflow
from dist_xgboost.constants import (
experiment_name,
model_fname,
model_registry,
preprocessor_fname,
)
def clean_up_old_runs():
# Clean up old MLflow runs.
os.path.isdir(model_registry) and shutil.rmtree(model_registry)
# mlflow.delete_experiment(experiment_name)
os.makedirs(model_registry, exist_ok=True)
def log_run_to_mlflow(model_config, result, preprocessor_path):
# Create a model registry in user storage.
mlflow.set_tracking_uri(f"file:{model_registry}")
# Create a new experiment and log metrics and artifacts.
mlflow.set_experiment(experiment_name)
with mlflow.start_run(description="xgboost breast cancer classifier on all features"):
mlflow.log_params(model_config)
mlflow.log_metrics(result.metrics)
# Selectively log just the preprocessor and model weights.
with TemporaryDirectory() as tmp_dir:
shutil.copy(
os.path.join(result.checkpoint.path, model_fname),
os.path.join(tmp_dir, model_fname),
)
shutil.copy(
preprocessor_path,
os.path.join(tmp_dir, preprocessor_fname),
)
mlflow.log_artifacts(tmp_dir)
clean_up_old_runs()
log_run_to_mlflow(model_config, result, preprocessor_path)
2025/04/16 21:07:07 INFO mlflow.tracking.fluent: Experiment with name 'breast_cancer_all_features' does not exist. Creating a new experiment.
启动 MLflow 服务器以查看实验。
mlflow server -h 0.0.0.0 -p 8080 --backend-store-uri {model_registry}
要查看仪表板,请转到 **Overview tab** > **Open Ports** > 8080。
您还可以查看 Ray Dashboard 和 Train 工作负载仪表板。
您可以从注册表中检索最佳模型。
from dist_xgboost.data import get_best_model_from_registry
best_model, artifacts_dir = get_best_model_from_registry()
artifacts_dir
'/mnt/user_storage/mlflow/290203875164933232/eb2666ca6cee4792bfda41a02b194d87/artifacts'
生产部署#
您可以将训练工作负载包装为生产级的 Anyscale Job。有关更多详细信息,请参阅 API 参考。
from dist_xgboost.constants import root_dir
os.environ["WORKING_DIR"] = root_dir
然后使用 anyscale CLI 命令提交作业。
%%bash
# Production batch job -- note that this is a bash cell
! anyscale job submit --name=train-xboost-breast-cancer-model \
--containerfile="${WORKING_DIR}/containerfile" \
--working-dir="${WORKING_DIR}" \
--exclude="" \
--max-retries=0 \
--wait \
-- cd notebooks && jupyter nbconvert --to script 01-Distributed_Training.ipynb && ipython 01-Distributed_Training.py
Output
(anyscale +0.9s) Submitting job with config JobConfig(name='train-xboost-breast-cancer-model', image_uri=None, compute_config=None, env_vars=None, py_modules=None, py_executable=None, cloud=None, project=None, ray_version=None, job_queue_config=None).
(anyscale +2.6s) Uploading local dir '/home/ray/default/e2e-xgboost' to cloud storage.
(anyscale +3.8s) Including workspace-managed pip dependencies.
(anyscale +4.2s) Job 'train-xboost-breast-cancer-model' submitted, ID: 'prodjob_bkbpnmhytt3ljt8ftlnyumjxdj'.
(anyscale +4.2s) View the job in the UI: https://console.anyscale.com/jobs/prodjob_bkbpnmhytt3ljt8ftlnyumjxdj
(anyscale +4.2s) Use `--wait` to wait for the job to run and stream logs.
扩展策略#
Ray Train 的一个主要优势是其能够轻松扩展训练工作负载。通过调整 ScalingConfig,您可以优化资源利用率并缩短训练时间。
扩展示例#
多节点 CPU 示例: 4 个节点,每个节点 8 个 CPU。
scaling_config = ScalingConfig(
num_workers=4,
resources_per_worker={"CPU": 8},
)
单节点多 GPU 示例: 1 个节点,8 个 CPU 和 4 个 GPU。
scaling_config = ScalingConfig(
num_workers=4,
use_gpu=True,
)
多节点多 GPU 示例: 4 个节点,每个节点 8 个 CPU 和 4 个 GPU。
scaling_config = ScalingConfig(
num_workers=16,
use_gpu=True,
)
重要提示:对于多节点集群,您必须在
run_config中指定一个共享存储位置,例如云存储或 NFS。使用本地路径会在检查点期间引发错误。trainer = XGBoostTrainer( ..., run_config=ray.train.RunConfig(storage_path="s3://...") )
工作进程配置指南#
最佳工作进程数量取决于工作负载和集群设置。
对于仅 CPU 训练,通常每个节点使用一个工作进程。XGBoost 可以通过线程利用多个 CPU。
对于多 GPU 训练,每个 GPU 使用一个工作进程。
对于异构集群,请考虑 CPU 数量的最大公约数。
GPU 加速#
要使用 GPU 进行训练:
使用
use_gpu=True启动每个 GPU 一个 Actor。设置与 GPU 兼容的参数,例如,XGBoost 的
tree_method="gpu_hist"。将 CPU 平均分配给每台机器上的 Actor。
示例:#
trainer = XGBoostTrainer(
scaling_config=ScalingConfig(
# Number of workers to use for data parallelism.
num_workers=2,
# Whether to use GPU acceleration.
use_gpu=True,
),
params={
# XGBoost specific params.
"tree_method": "gpu_hist", # GPU-specific parameter
"eval_metric": ["logloss", "error"],
},
...
)
有关更高级的主题,请参阅:

